Fig. 2: ZFP462 elicits silencing function through interaction with G9A/GLP and HP1γ.
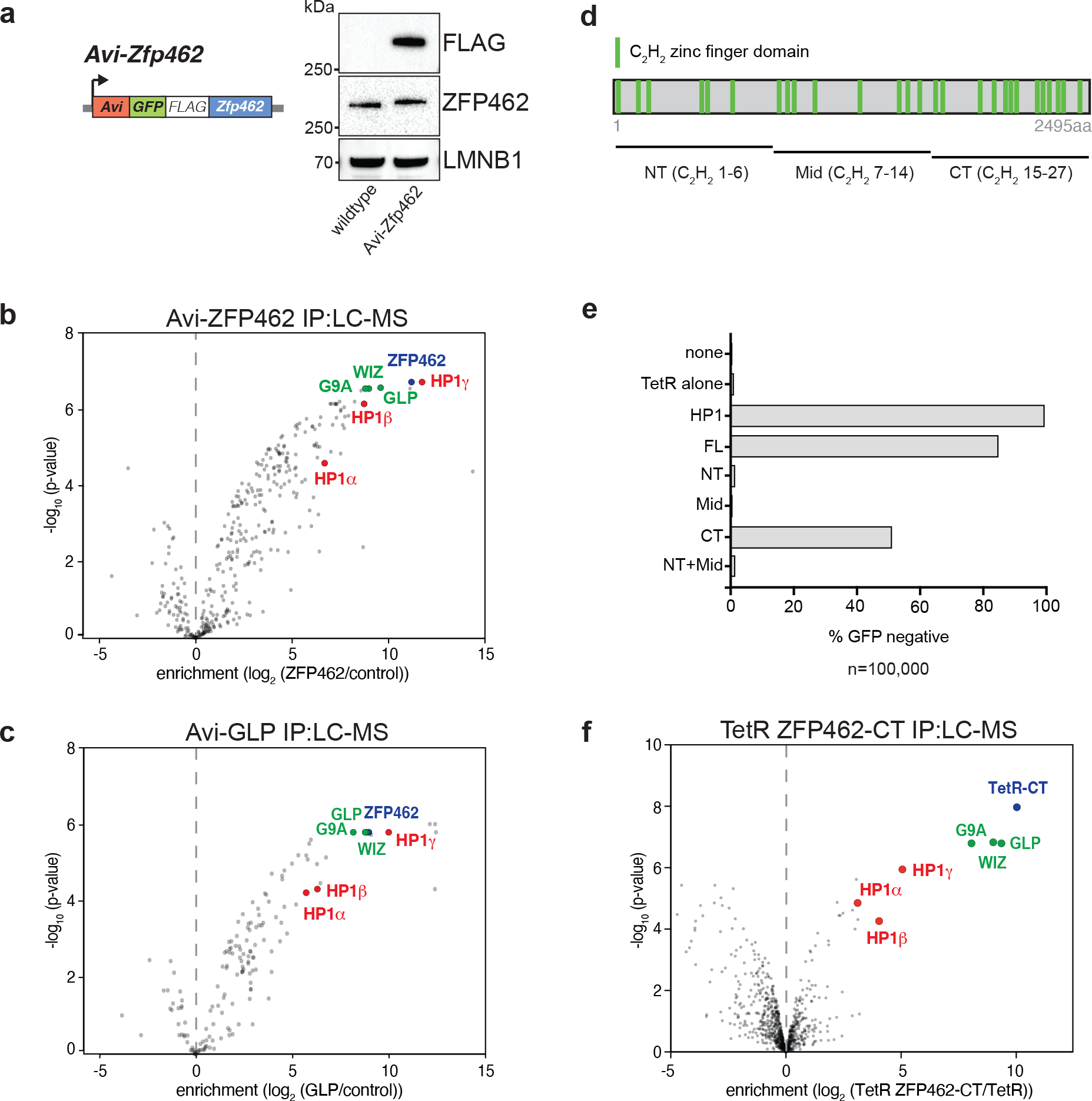
a) Design of Avi-Zfp462 ESCs and western blot validation. Mouse ESCs expressing Biotin ligase (BirA) were used to modify the endogenous Zfp462 gene by inserting the Avi-GFP-3XFLAG tag downstream of the translation start codon. Western blot with FLAG and ZFP462 antibodies confirms ZFP462 tagging. b) and c) LC-MS analysis of Avi-tagged ZFP462 and Avi-tagged GLP ESCs. Volcano plots show enrichment and corresponding significance of co-purified proteins. (n = three replicates). d) Scheme of ZFP462 protein depicts locations of 27 C2H2 zinc finger domains (green bars). Fragments used to generate TetR fusions for tethering in CiA Oct4 dual reporter assay are indicated below. e) Bar plot shows percentage of GFP-negative CiA Oct4 ESCs measured by flow cytometry in response to ectopic TetR fusion protein expression (y-axis). f) Volcano plot of LC-MS analysis compares enrichment and corresponding significance of co-purified proteins between TetR-FLAG-ZFP462-CT and TetR-FLAG (n = three replicates).
