FIGURE 2.
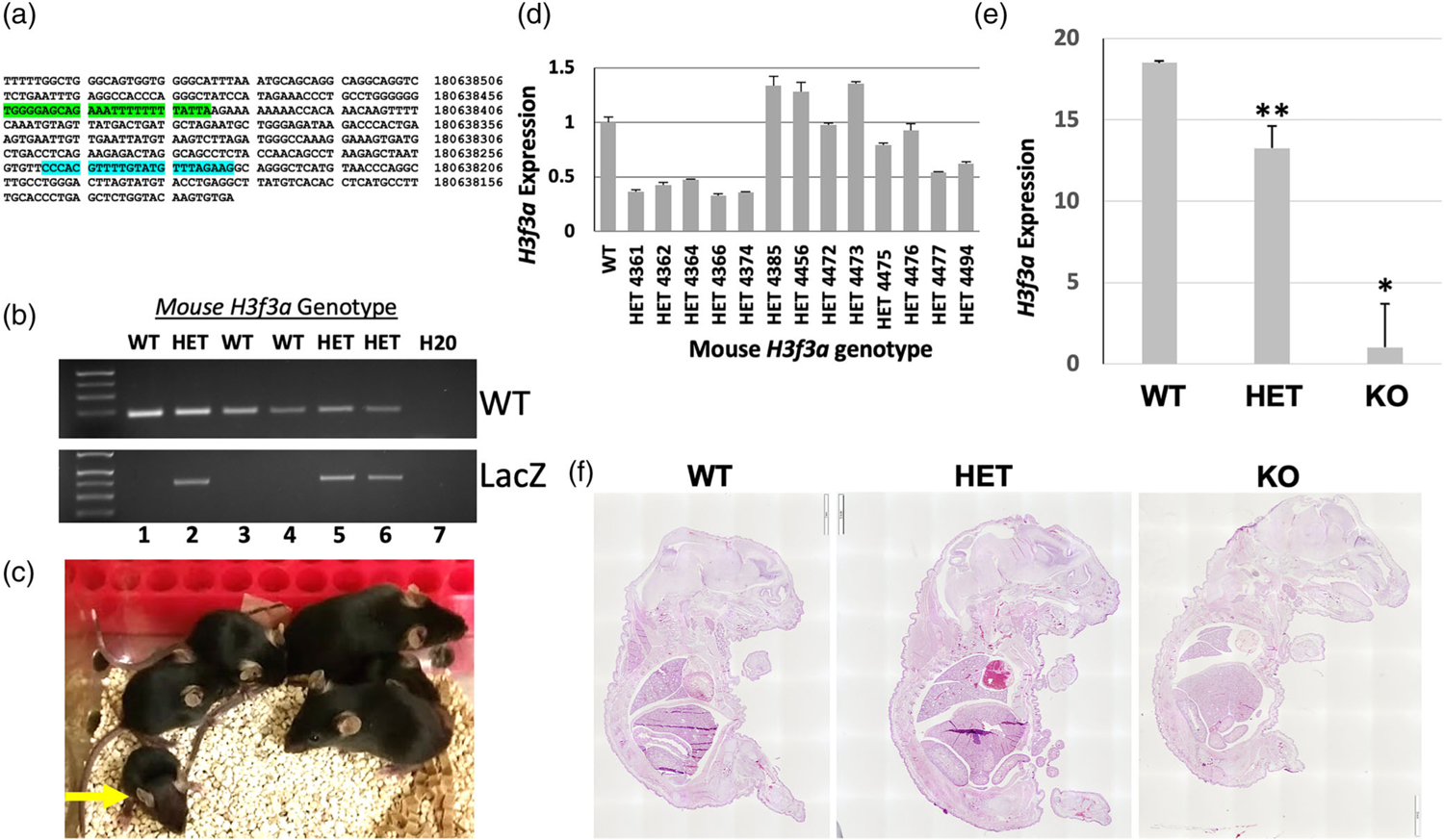
Phenotypes of H3f3a targeted mice and evidence of embryonic lethality. (a) Sequence of the WT H3f3a allele with WT genotyping primer binding sites highlighted from UCSC Browser (mm39). (b) Example of WT and knockout-first allele (LacZ) amplicons detected via gene-specific genomic PCR. (c) A representative litter of pups generated from heterozygous crosses. All surviving pups were WT or heterozygous. A small heterozygous pup at the left is indicated by the yellow arrow. (d) H3f3a RNA levels by RT-qPCR in WT and heterozygous pups; heterozygous H3f3a RNA levels are heterogeneous. (e) H3f3a RNA levels in WT, heterozygous, and null animal ear tissue samples. (f) Representative H&E stained sections of E18.5 littermate embryos from heterozygous intercrosses are shown. Error bars are the standard deviation of triplicate samples in (d–e) and p values for WT versus heterozygous and null are = .0002 and .002, respectively for ** and *
