Figure 3.
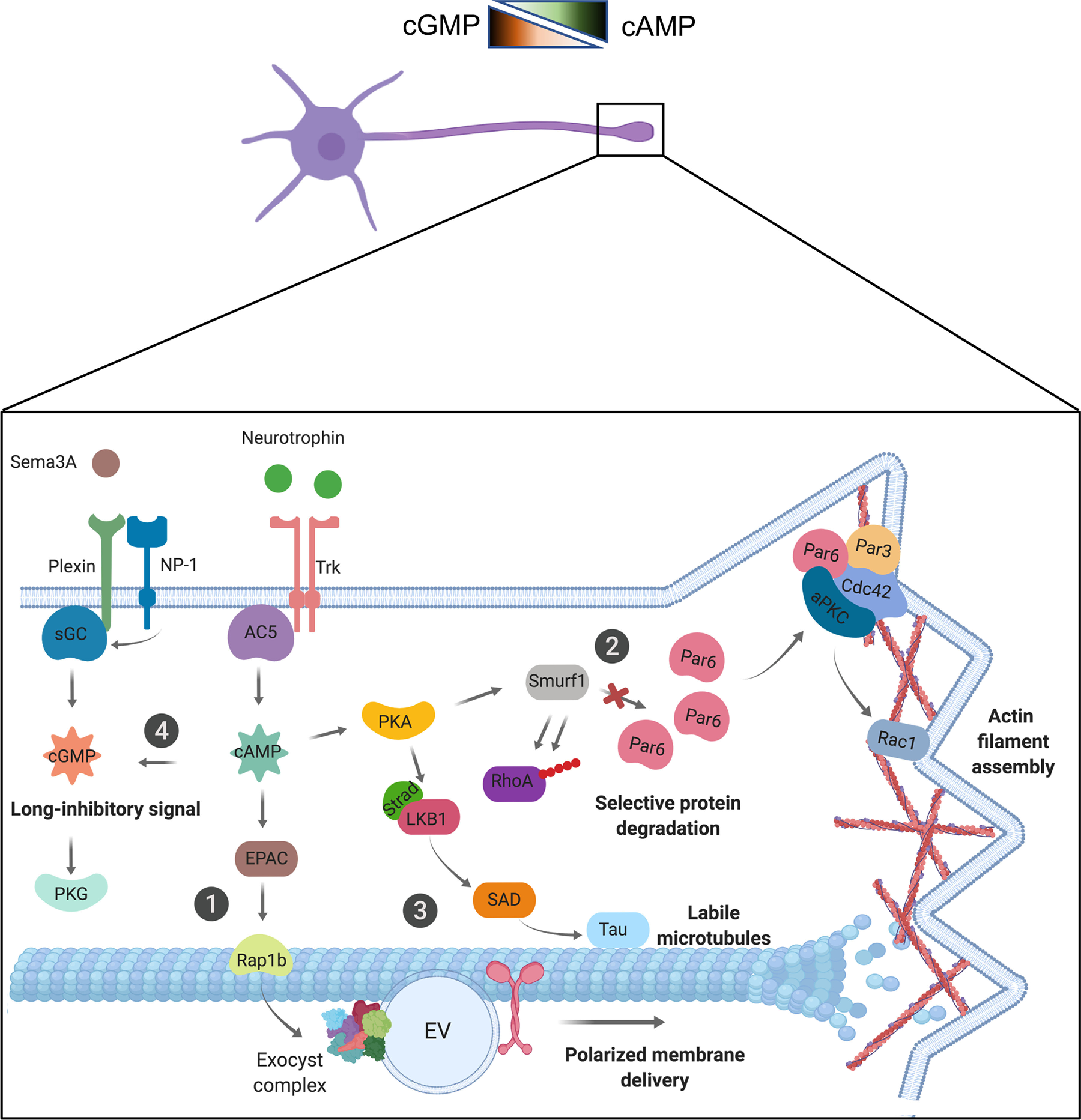
cAMP and cGMP signaling pathways involved in neuronal polarization. Top, Schematic representation of cAMP and cGMP gradients in neurons. Bottom, Diagram showing a growth cone. Trk activation by ligand binding activates adenylyl cyclase 5 (AC5), inducing the generation of cAMP. In contrast, inhibitory signals like Plexin or NP-1 induce the activation of soluble GC (sGC), triggering cGMP production. cAMP and cGMP impact several effectors to regulate axon elongation. ①, cAMP activates the EPAC-Rap1b signaling pathway controlling exocyst complex-mediated polarized membrane delivery, and ② PKA-Par complex-Rac1 signaling pathway, triggering actin filament assembly. ③, PKA also activates LKB1-tau signaling, increasing the labile microtubule fraction. ④, Finally, cAMP production induces a cGMP long-inhibitory signal, reducing cAMP levels in the soma and other neurites. EV, Exocytic vesicle.
