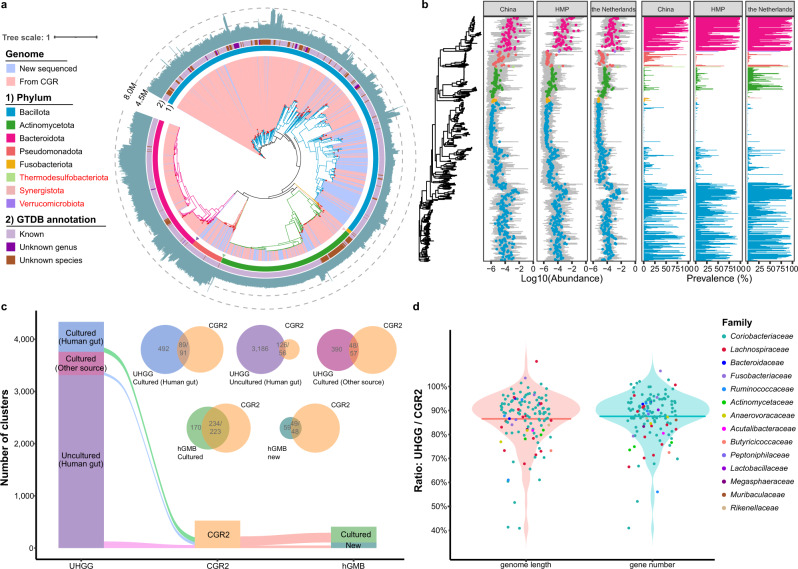
Fig. 1. Taxonomic profile of CGR2.
a Phylogenetic analysis of 3324 genomes. Color range indicates the 1804 newly sequenced genomes (blue) and the 1520 CGR genomes (pink). Singleton genomes are marked with red dots at the end of the clade. The first layer depicts the GTDB phylum annotation, the second layer describes the matching to the GTDB database at the species and genus level, and the circumferential bar plot (dark blue) illustrates the genome size. b Abundance and prevalence of 527 representative clusters in healthy cohorts of China, HMP, and the Netherlands. Gray box, Log10 (relative abundance); Dot, median of log10 (relative abundance); Bar, prevalence; Color, phylum. c Matching of CGR2 to the hGMB and UHGG genome collections. The Venn diagrams are colored according to the origin of the samples and the numbers are indicated. d The ratio of the genome length (median: 88.84%) and gene number (median: 89.33%) of the UHGG-Uncultured relative to CGR2 in the mapped genomes of each family. A dot represents a UHGG genome, and different colored dots indicate different family.