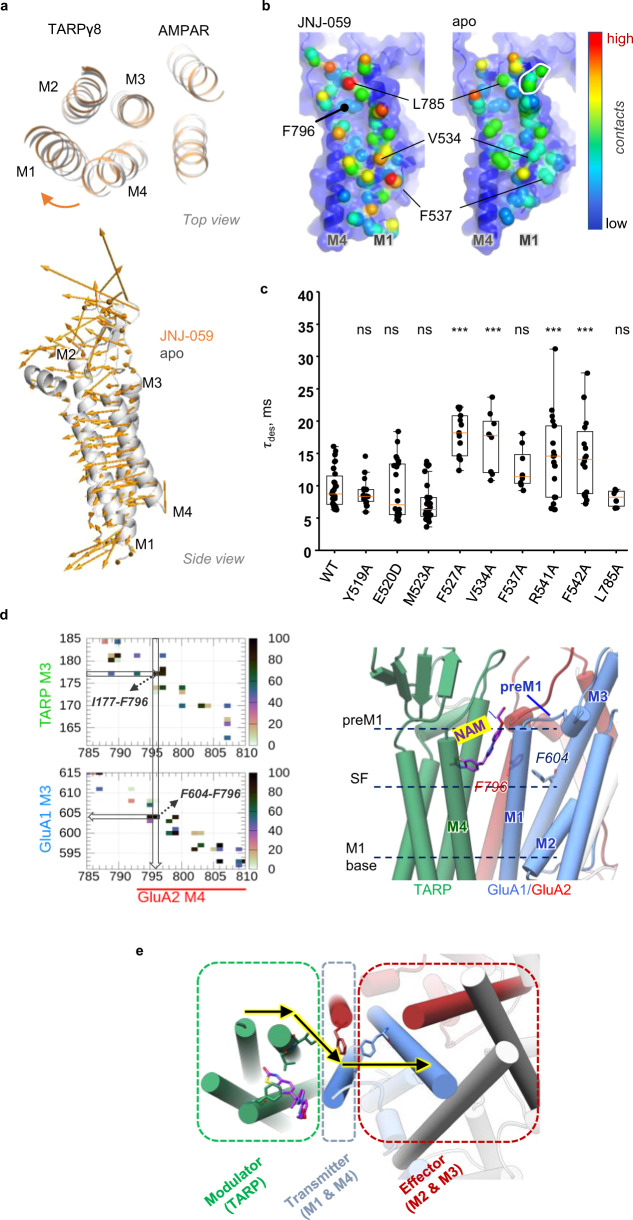
Fig. 5. NAMs trigger a global reorientation of TARP γ8.
a JNJ-059-induced rotation of γ8 helices M1, M2 and M4, relative to an apo structure (PDB: 7OCD). Alignment of the TMD sector of apo (grey) and JNJ-059-bound (orange) resting-state models. The vectors indicate the direction of γ8 in response to the NAM in both top and side views. Vectors were generated using the ‘modevectors’ script in PyMol. b TARP γ8 contact points along its binding site, the M4GluA2 and M1GluA1 helices. Contacted residues are coloured depending on the number of atoms contributing to the interaction (red: high; blue: low). Countacts were computed using ‘findNeighbors’ in ProDy’ with a 4.5 Å cutoff between heavy atoms74. c Box plots showing macroscopic desensitization τ for GluA1_γ8 wild type and mutants; each point is a τdes (WT: 9.7 ± 0.6 ms, n = 30; Y519A: 8.9 ± 0.5 ms, n = 18; E520D: 9.4 ± 1.0 ms, n = 22; M523A: 7.4 ± 0.6 ms, n = 27; F527A: 18.0 ± 0.9 ms, n = 13; V534A: 17 ± 2 ms, n = 8; F537A: 13 ± 1 ms, n = 8; R541A: 16 ± 1 ms, n = 24; F542A: 15 ± 1 ms, n = 21; L785A: 8.0 ± 0.5 ms, n = 6; mean ± SEM) obtained by fitting the decaying phase of whole-cell currents with a single exponential. Boxes show the 25th/75th percentiles and whiskers indicate the furthest points that fall within 1.5 times of interquartile range from the 25th/75th percentiles. The horizontal line in each box shows the median value. Asterisks summarize one-way ANOVA test, Dunnett correction was used for multiple comparisons to wild type receptor (***p ≤ 0.001 and ‘ns’ for p > 0.05). d High-frequency residue contacts forming a potential pathway from the NAM binding site to the gate. Left panel: TARP-GluA2 (top) and GluA2-GluA1 (bottom) contact maps for the JNJ-059 resting state MD simulation, suggesting a route from TARP Ile177 via GluA2 Phe796 to GluA1 (see “Methods” for further detail). Middle panel: Pathway residues relative to key regions in the AMPAR pre-M1, selectivity filter (SF), and cytosolic base of M1. e Overall model suggesting that allosteric information from the TARP (Modulator) is communicated via the AMPAR peripheral M1 + M4 helices (Transmitter) to the M3 gate (Effector). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.