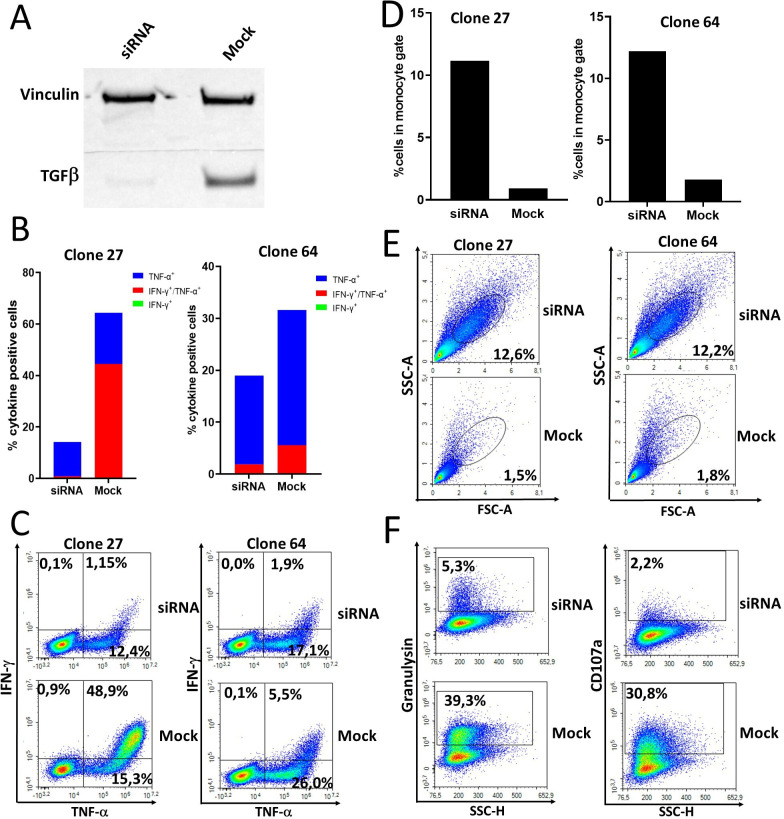
Figure 6.
T cells specific for TGF-β-15 from a patient with pancreatic cancer with complete response to immune checkpoint inhibitor and stereotactic body radiotherapy recognize and kill autologous regulatory myeloid cells in a TGF-β-dependent manner. (A) Western blot analysis of TGF-β expression by regulatory myeloid cells that had been either mock transfected or transfected with TGF-β siRNA. Monocytes were stimulated for 4 days with GM-CSF and TGF-β1, then transfected and restimulated with GM-CSF and TGF-β1 for 2 days before harvesting and lysing of cells. (B) Two TGF-β-15 specific T-cell clones were stimulated with siRNA or mock transfected autologous regulatory myeloid cells in an intracellular cytokine staining (ICS) assay. (C) Contour plot of results shown in B. (D) The amount of regulatory myeloid cells detected in the forward-side scatter plot during the ICS experiment was quantified. (E) Contour plot of results shown in D. (F) Expression of the cytotoxicity markers CD107a and granulysin by TGF-β-15 specific T-cell clones on stimulation with autologous regulatory myeloid cells. GM-SCF, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating-factor; IFN, interferon-γ; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; TNF, tumor necrosis factor-α.