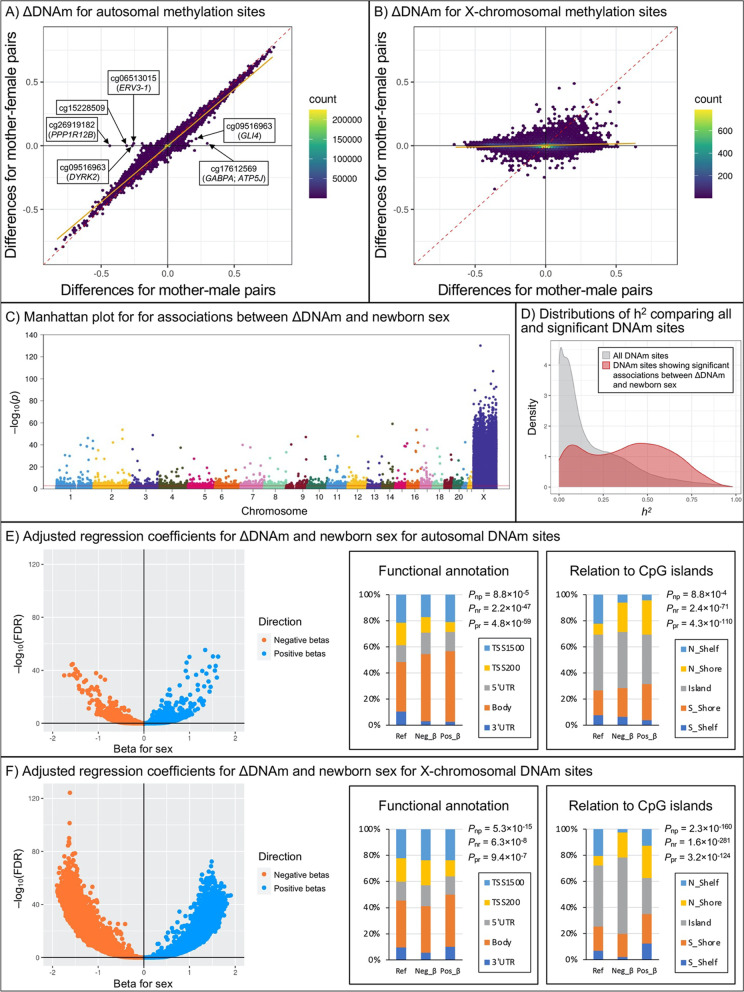
Fig. 3.
Sex differences in associations between differences in maternal-neonatal methylation levels (ΔDNAm) and newborn sex at individual DNAm sites. We first illustrated differences in maternal–neonatal methylation levels of individual DNAm sites (ΔDNAm) on A) autosomes and B) the X chromosome, stratified by newborn sex. The orange regression lines represent the concordance of ΔDNAm for mother–male and mother–female pairs. Then, we used C) Manhattan plot to show the distribution of p values of associations between ΔDNAm and newborn sex; the red horizontal line marks FDR = 0.05. We also used D) density plot to compare the heritability of DNAm sites showing significant associations between ΔDNAm and newborn sex to that of DNAm sites across the whole genome using data from a published study on DNAm quantitative trait loci [25], but only the heritability of autosomal DNAm sites was available. Finally, we illustrated the regression coefficients for E) autosomal and F) X-chromosomal DNA sites; blue dots represent positive betas (mother–male differences larger than mother–female differences), while orange dots represent negative betas (mother–male differences smaller than mother–female differences). We also presented the percentages of function annotation and the relation to CpG island for individual E) autosomal and F) X-chromosomal DNA sites, and compared the distributions between genome-wide references, negative betas, and positive betas using chi-square test. Linear regression models were adjusted for maternal age at delivery, maternal race/ethnicity, maternal smoking, preterm birth, type of delivery, and 37 surrogate variables. DNAm, DNA methylation; ΔDNAm, differences in maternal-neonatal methylation levels; h2, heritability; Ref, the distributions of mapped genes of all DNAm sites that were included in the analysis; Neg_β, the distributions of mapped genes of DNAm sites that showed significant negative associations between ΔDNAm and newborn sex; Pos_β, the distributions of mapped genes of DNAm sites that showed significant positive associations between ΔDNAm and newborn sex; Pnp, Pnr, and Ppr represent p-values comparing the distributions of functional annotations for negative βs vs. positive βs, negative βs vs. references, and positive βs vs. references, respectively