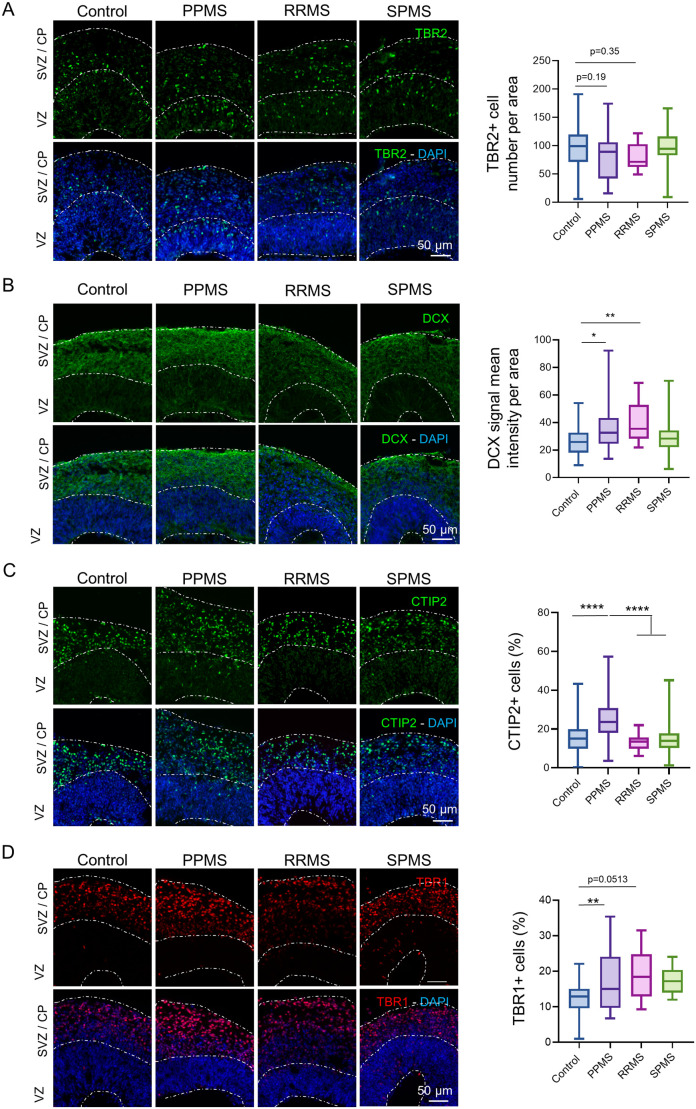
Fig. 3.
MS organoids exhibits larger neural progenitor population. (A) Representative images of an immunofluorescence against the IPC marker TBR2 in c-organoids at D42. Quantifications of TBR2+ cell number in cortical structure of organoids at D42 did not show any significant difference between the different conditions [one-way ANOVA, F (3, 149)=2.162, P= 0.0949, followed by a Tukey post hoc test]. (B) Representative images of an immunofluorescence against the neuroblast marker DCX in c-organoids at D42. DCX immunofluorescence mean intensity was measured and compared in each condition. A significant increase of DCX immunostaining intensity was measured in PPMS and RRMS compared to control, while no difference was observed for SPMS organoids (Kruskal–Wallis test, H value=18.01, P=0.0004, followed by a Dunn's post hoc test). (C) Representative images of an immunofluorescence against the deep-layer cortical neuron marker CTIP2 in c-organoids at D42. Quantification of the percentage of CTIP2+ cells in c-organoids revealed a significant higher expression of CTIP2 in PPMS compared to control, RRMS and SPMS (Kruskal–Wallis test, H value=36.94, P<0.0001, followed by a Dunn's post hoc test). (D) Representative images of an immunofluorescence against the early-born cortical neuron marker TBR1 in c-organoids at D42. Quantification of TBR1+ cell percentage in organoid cortical structure showed a significant higher expression of TBR1+ cells in PPMS compared to control [one-way ANOVA, F (3, 94)=4.701, P= 0.0042, followed by a Tukey's multiple comparisons test]. To ensure quantification consistency, analyzed cortical area were cropped from the original picture to a 250 µm wide×300 µm image, spanning all cortical layers (VZ, SVZ, and CP). n=3 organoids per cell line from three to four independent experiments each. One to two cortical structure were analyzed per organoid. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.