Fig. 1.
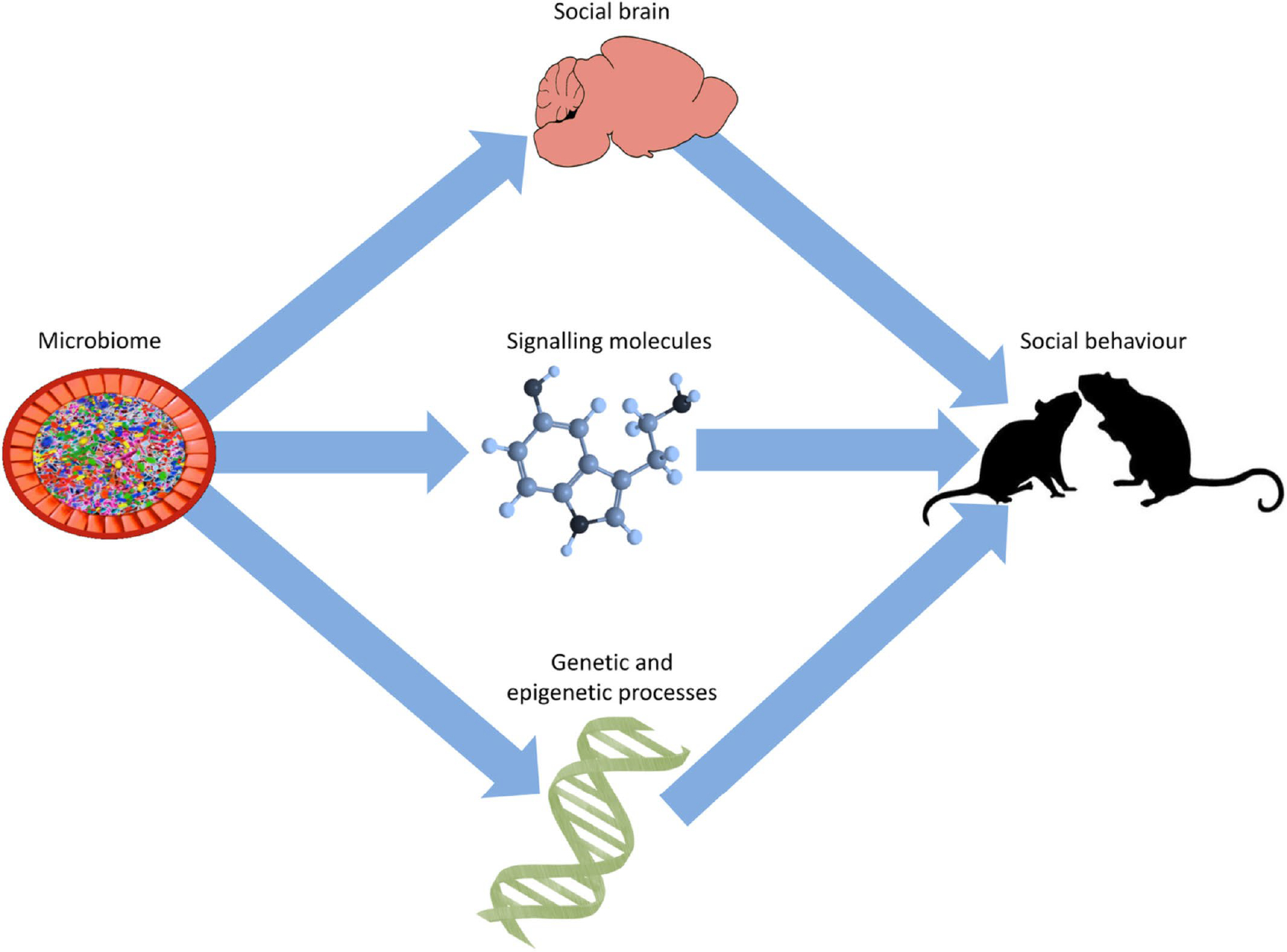
Proposed physiological mediators of the microbiome–sociality relationship. We propose that the microbiome affects host social behaviour via regulation of: (i) the structure and function of the social brain, (ii) signalling molecules known to be involved in social behaviour, and (iii) host genetic and epigenetic processes. In addition to the arrows depicted in the diagram, the microbiome’s effects on the structure of the social brain and its signalling molecules may, at least in part, be due to genetic and epigenetic mechanisms.
