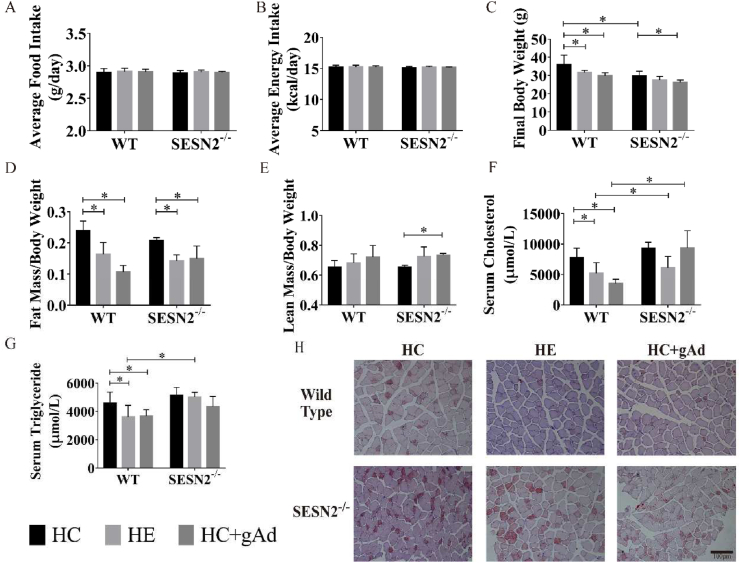
Fig. 2.
Effects of exercise or globular adiponectin on energy metabolism in mice fed on high-fat diet.
Wild-type and SESN2−/− mice were randomly allocated to sedentary or exercise group (75% O2max intensity, 12 m/min, 1 h/day, 5 days/week) or gAd injection group (5 μg/kg body weight, 7 days/week), feeding with 60% high-fat diet. Average food intake and average energy intake were determined. Additionally, final body weight (C), fat mass/body weight (D) and lean mass/body weight (E) were measured. Serum total cholesterol (TC) (F) and triglycerides TG (G) were measured with ELISA kits. Representative images of oil red staining within muscle fibers of each group (H). (n = 6,6,5,5,6,4 for WT-HC, WT-HE, WT-HC + gAd, SESN2−/−-HC, SESN2−/−-HE, SESN2−/−-HC + gAd, respectively). Data are shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD). ∗, p < 0.05. HC - HFD control, HE - HFD exercise group, HC + gAd - HFD gAd inject group, WT - wild type, SESN2 - Sestrin2.