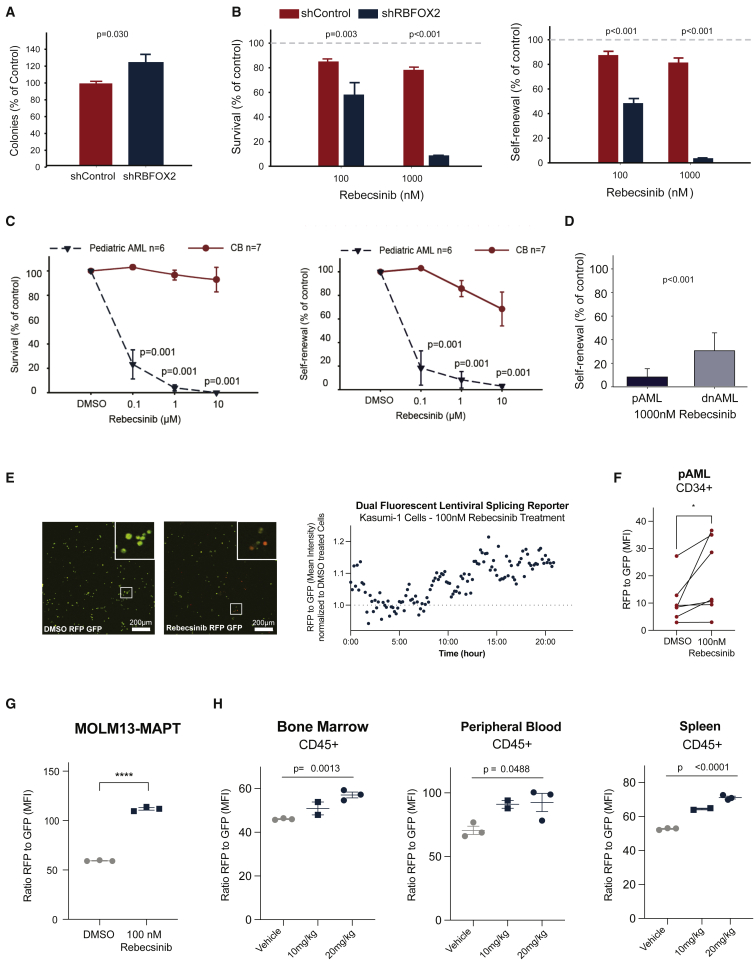
Figure 6.
Rebecsinib inhibition of pAML LSC survival and self-renewal
(A) Colony assay of CD34+ cord blood cells in long-term stromal co-cultures following lentiviral shRNA control (shControl, n = 7 biological replicates) or shRNA knockdown of RBFOX2 (shRBFOX2, n = 7 biological replicates; Student’s t test, p = 0.03). Data represent mean ± SD.
(B) Percent colony survival and self-renewal (replating) of CD34+ cord blood samples after treatment with 100 or 1,000 nM of Rebecsinib normalized to vehicle-treated controls. Mean colony percentages ± SD are shown for each treatment condition (n = 7 biological replicates). Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA (survival [left] 100 nM Rebecsinib shControl versus shRBFOX2 p = 0.003, 1,000 nM Rebecsinib shControl versus shRBFOX2 p < 0.001; self-renewal [right] 100 nM Rebecsinib shControl versus shRBFOX2 p < 0.001, 1,000 nM Rebecsinib shControl versus shRBFOX2 p < 0.001).
(C) Survival and self-renewal of CD34+ cells derived from pAML (n = 6 biological replicates) or cord blood (CB) (n = 7 biological replicates) in long-term stromal co-cultures. Data represent mean ± SD for each treatment condition. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA (survival [left] 0.1 μM Rebecsinib pAML versus CB p = 0.001, 1 μM Rebecsinib pAML versus CB p = 0.001, 10 μM Rebecsinib pAML versus CB p = 0.001; self-renewal [right] 0.1 μM Rebecsinib pAML versus CB p = 0.001, 1 μM Rebecsinib pAML versus CB p = 0.001, 10 μM Rebecsinib pAML versus CB p = 0.001).
(D) Self-renewal of CD34+ pAML (n = 6 biological replicates) versus adult dnAML (n = 9 biological replicates) treated with Rebecsinib. Data represent mean ± SD for each treatment condition. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA (pAML versus adult dnAML p < 0.001).
(E) Representative fluorescence microscopic imaging analysis of the pAML cell line Kasumi-1 cells stably transduced with the lentiviral pCDH-EF1-IRES-Puro MAPT dual-fluorescence splicing reporter treated with (left) DMSO (scale bar, 200 μm) and (middle) 100 nM Rebecsinib (scale bar, 200 μm). Right: the ratio of RFP/GFP was quantified using Volocity software (Quorum Technologies) following Rebecsinib treatment and normalized to DMSO vehicle controls (n = 1).
(F) FACS analysis of RFP/GFP MFI in the live cell population of CD34+ selected pAML patient samples treated with 100 nM Rebecsinib for 72 h (n = 6 biological replicates, Student's t test, p = 0.016).
(G) FACS analysis of RFP/GFP MFI in MOLM13 (a leukemia cell line derived from a 20-year-old male) cells stably transduced with the lentiviral pCDH-EF1a-IRES-Puro MAPT dual-fluorescence splicing reporter and treated in vitro with Rebecsinib (100 nM) versus DMSO (n = 3 technical replicates, data represent mean ± SEM, Student's t test, p < 0.0001).
(H) MOLM13-MAPT splicing reporter stably transduced cells were engrafted into irradiated NSG-SGM mice, treated with vehicle (n = 3 biological replicates) or Rebecsinib (10 or 20 mg/kg; n = 2, n = 3 technical replicates), and sacrificed 24 h post-treatment. The ratio of RFP/GFP MFI in live, human CD45+ cells in bone marrow, spleen, and peripheral blood was quantified by FACS analysis using a MACS Quant instrument and FlowJo software. Data represent mean ± SEM for each treatment condition. Statistical analyses were performed using unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test (bone marrow [left] vehicle versus 20 mg/kg p = 0.0013, peripheral blood [middle] vehicle versus 20 mg/kg p = 0.0488, spleen [right] vehicle versus 20 mg/kg p < 0.0001). See also Figure S6.