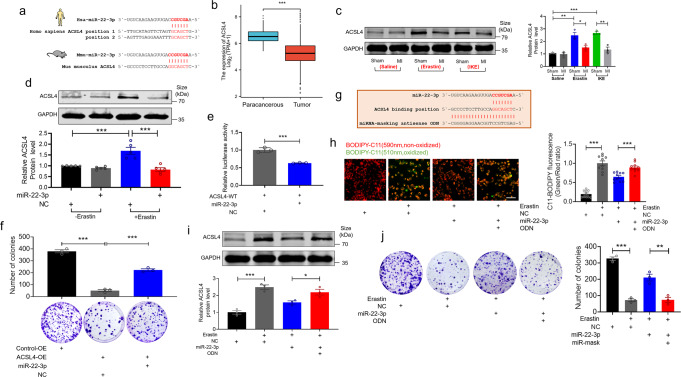
Fig. 7.
Direct interaction between miR-22-3p and ferroptosis-related gene ACSL4. a The sequence of miR-22-3p and the potential binding site of ACSL4 mRNA; b ACSL4 gene expression in lung cancer tissues and paracancerous tissues from TCGA database; c, d The protein expression levels of ACSL4 were determined by western blot in (c) subcutaneous xenograft tissues was determined (N = 3/group) and in (d) LLC cells after transfecting with miR-22-3p and NC in the presence of erastin (N = 5 independent experiments); e Luciferase activity assay was performed to confirm the ACSL4 mRNA was directly bound to miR-22-3p in HEK-293T cells (N = 3 independent experiments); f LLC cells were co-transfected with ACSL4 overexpression/empty constructs and miR-22-3p mimics/NC for 24 h. Representative images and quantitative results of LLC cancer cell colonies (N = 3 independent experiments); g Complementarity between miR-22-3p seed sequence and the ACSL4 mRNA, the miRNA-masking antisense (ODN-22-3p) was designed to be fully complementary to the miR-22-3p targeting sequence on ACSL4; h–j LLC cells were transfected with miR-22-3p mimics and ODN in the presence of erastin for 24 h. h Analysis of lipid-ROS using C11 BODIPY 581/591 fluorescence staining (Bar: 40 μm), Red, non-oxidized form of C11-BODIPY; Green, oxidized form of C11-BODIPY. Each data point represents the ratio of oxidized C11 to non-oxidized C11 signal (N = 10 from 3 independent experiments); i The protein expression levels of ACSL4 were determined by western blot (N = 3 independent experiments); j Representative images and quantitative results of LLC cancer cell colonies (N = 3 independent experiments). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001