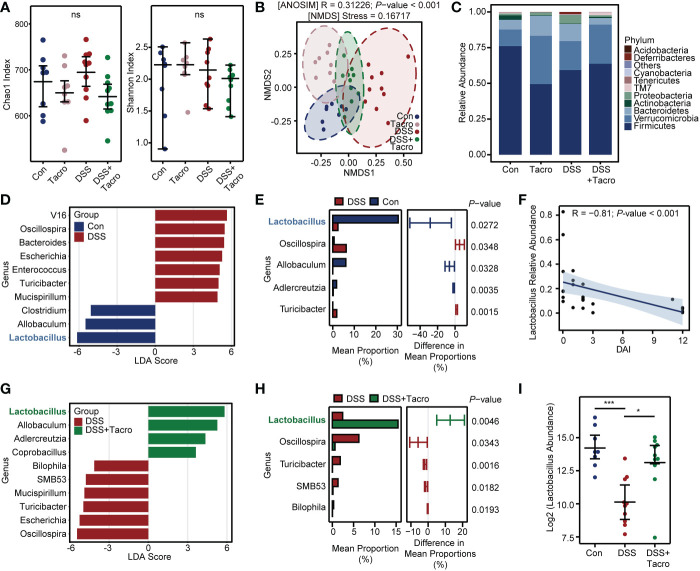
Figure 2.
Tacrolimus triggered a significant increase in the genus Lactobacillus in colitis. (A) The microbial α-diversity in the cecal contents of mice. (B) β-diversity analysis based on the NMDS and ANOSIM methods. (C) Relative abundance of gut bacterial composition at the phylum level. (D) The LDA scores between the control and DSS-treated groups at the genus level. The threshold was set as 3. (E) The significantly different bacteria between the control and DSS-treated groups evaluated by STAMP. (F) Correlation analysis between Lactobacillus relative abundance and DAI score. A total of 28 samples from the Con, DSS and DSS + Tacro groups were included in this analysis. (G) The LDA scores of the DSS + Tacro group when compared with the DSS group at the genus level. (H) Significantly different genera between the DSS and DSS + Tacro groups evaluated by STAMP. (I) Lactobacillus abundance in log 2 scale among different treatment groups. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ns, no significance; Con, control; DSS, dextran sulfate sodium; Tacro, 10 mg/kg tacrolimus; NMDS, nonmetric multidimensional scaling; LDA, linear discriminant analysis; STAMP, statistical analysis of metagenomic profile; DAI, disease activity index.