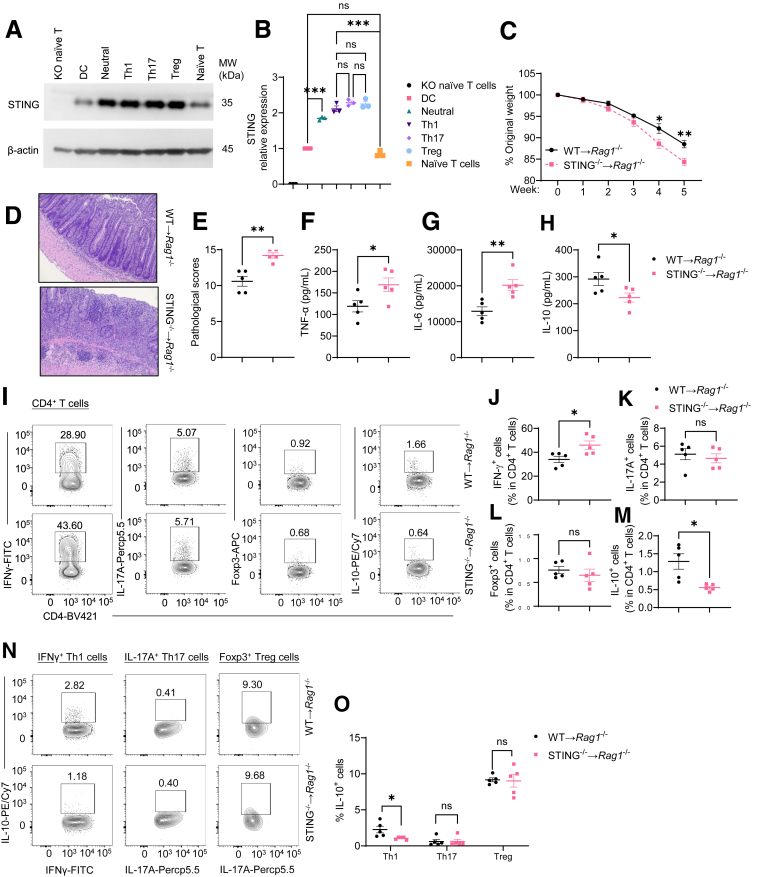
Figure 2.
STING-deficient CD4+T cells induce more severe colitis in Rag1–/–mice. (A, B) STING and β-actin levels were determined in WT dendritic cells (DCs), naïve WT T cells, naïve STING–/– (knockout [KO]) T cells, and WT T cells cultured on neutral, Th1, Th17, and Treg conditions by Western blot (n = 3/group). (A) Western blot bands. (B) STING relative expression. (C–O) WT or STING-deficient CD4+ CD45Rbhi T cells were intravenously transferred into Rag1–/– mice (n = 5/group). The recipient Rag1–/– mice were sacrificed 5 weeks later. (C) The weight changes of the recipient Rag1–/– mice. (D) Representative intestinal histological images. (E) Pathological scores. (F) Intestinal TNF-α production. (G) Intestinal IL-6 production. (H) Intestinal IL-10 production. (I) Representative flow cytometry plots of intestinal IFNγ+, IL-17A+, Foxp3+, and IL-10+ CD4+ T cells. (J–M) Dot plots of IFNγ+, IL-17A+, Foxp3+, and IL-10+ CD4+ T cells. (N) Representative flow cytometry plots of IL-10+ Th1, IL-10+ Th17, and IL-10+ Treg cells. (O) Dot plots of IL-10+ Th1, IL-10+ Th17, and IL-10+ Treg cells. Data were shown as mean ± SEM. (A, B) Data were pooled from 3 independent experiments. (C–O) One representative of 3 independent experiments. (A) 1-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; (C, F, G, I, J, K, L, M, N) unpaired Student’s t test; (E) Mann-Whitney U test. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001. ns, not significant.