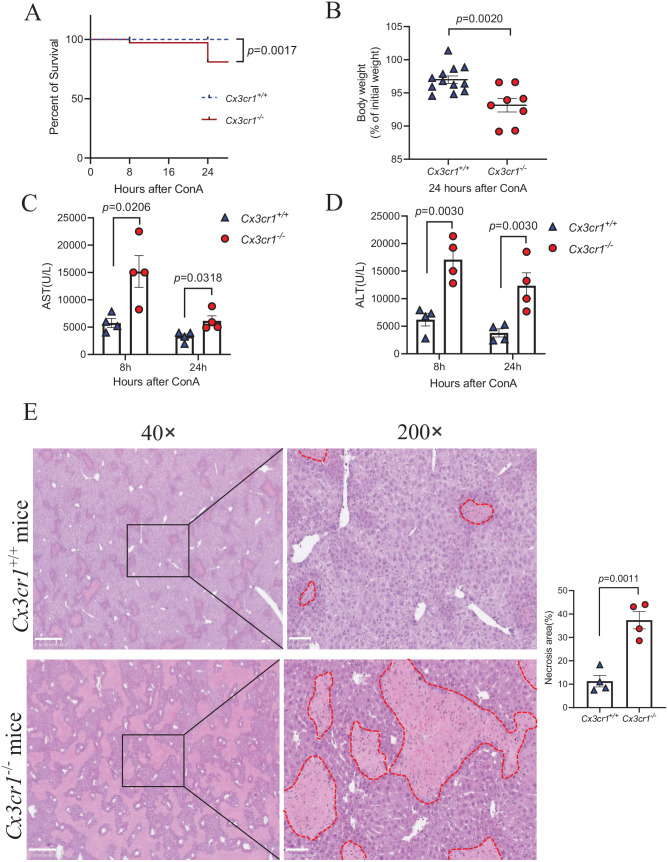
Figure 1.
Increased Con A-induced liver injury in Cx3cr1−/− mice compared to wild-type Cx3cr1+/+ mice.
Immune-mediated hepatitis was induced by intravenous injection with 15 mg/kg body weight of ConA in Cx3cr1+/+ and Cx3cr1−/− mice. (A) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of Cx3cr1+/+ (n = 12) and Cx3cr1−/− (n = 12) mice. (B) Cx3cr1+/+ (n = 12) and Cx3cr1−/− (n = 8) mice were weighed before ConA injection (initial body weight), and before euthanasia (final body weight). The data of A and B were combined from three independent experiments. (C, D) Serum AST and ALT were measured at 8 and 24 h after ConA treatment (Cx3cr1+/+ n = 4; Cx3cr1−/− n = 4). (E) Left: Representative H&E staining in the liver of ConA-treated Cx3cr1+/+ mice and Cx3cr1−/− mice. (original magnification: 40× and 200×). The scale bars are 500 μm (40×) and 100 μm (200×), respectively. Right: The quantification of liver necrosis area. (A color version of this figure is available in the online journal.)