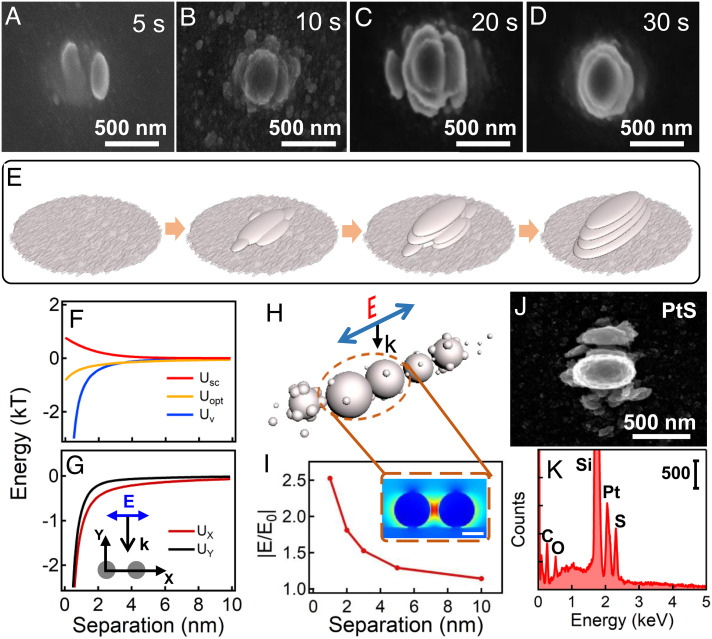
Fig. 2.
Mechanism of polarization-directed oriented growth of platinum oxide nanopillars. (A–E) Evolution kinetics of platinum oxide nanopillars. SEM images of the platinum oxide nanoparticles at different irradiation time (A) 5 s, (B) 10 s, (C) 20 s, (D) 30 s. Irradiation power: 1 mW. (E) Schematic of the growth process. (F) Energy profile of the platinum oxide nanoparticles with optical dipole (Uopt), screening charge (Usc) and van der Waals (Uv) interactions and (G) the total energy along X and Y axis. The polarization is along X axis. Ux= Uopt + Usc + Uv and UY= Usc + Uv. (H) Mechanistic illustration on the polarization-induced charge dipole interaction. (I) Change of near-field enhancement with separation between the platinum oxide nanoparticles. Inset is the electric near field profile of two platinum oxide nanoparticles (dia. ~20 nm) with separation of 2 nm. (Scale bar is 10 nm.) (J) SEM images of PtS nanopillars formed by irradiating the mixture of K2PtCl4 and Na2S2O3 for 30 s (Irradiation power: 2 mW) and (K) corresponding EDS.