FIGURE 3.
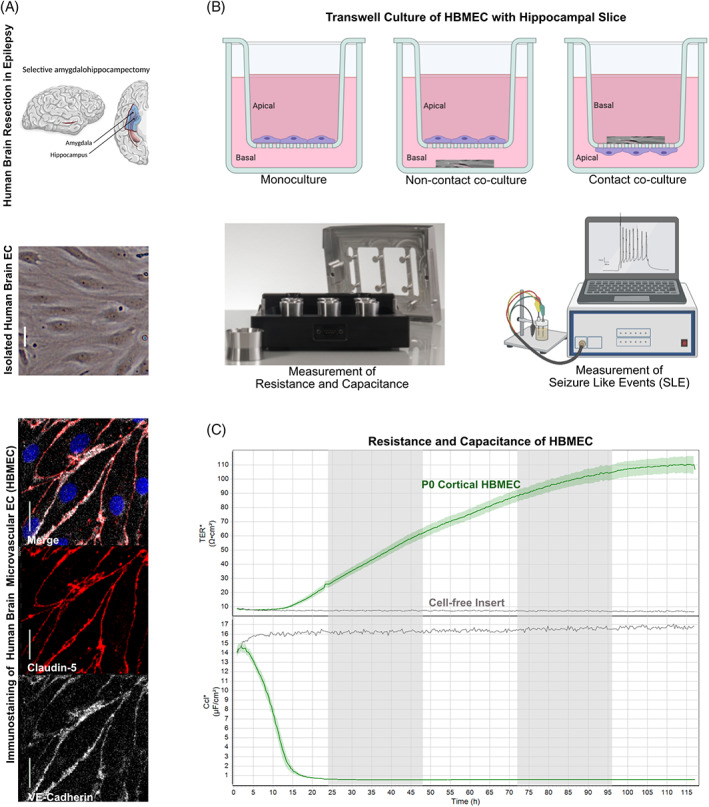
In vitro BBB co‐culture model of hippocampal slices with brain endothelial cells. (A) Brain endothelial cells (EC) isolated from the temporal cortex surgically resected from TLE patients by selective amygdalahippocampectomy (top panel; adapted from [139]) exhibit the classic spindle shape of brain ECs (middle panel) and express the BBB markers VE‐cadherin (white) and claudin‐5 (red). Scale bars 10 mm. (B) The isolated brain ECs cultured on transwell inserts represent a BBB in vitro monoculture model. The co‐culture of the cortical ECs on the transwell insert membrane (apical) with the hippocampal tissue slice obtained from TLE patient surgery in the bottom chamber (basal) represent the non‐contact co‐culture model for the BBB in vitro. The co‐culture of the hippocampal slice on top of the transwell insert membrane (basal) with the cortical ECs on the bottom of the insert membrane (apical) represents a contact co‐culture BBB in vitro epilepsy model. Impedance measurements performed on these transwell inserts for the in vitro BBB model in a cellZscope (nanoAnalytics) device provide resistance and capacitance values reflecting BBB function. Electrophysiological recordings from the hippocampal slice either from the insert or from the bottom chamber provide measurements of seizure‐like events from the epileptic tissue. (C) Representative transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER) and capacitance (Ccl) values from a monolayer of cortical brain ECs (green line) isolated from a TLE patient show high resistance and low capacitance values indicating a functional monoculture BBB model in vitro (as in A) compared to the cell‐free insert (black line).
