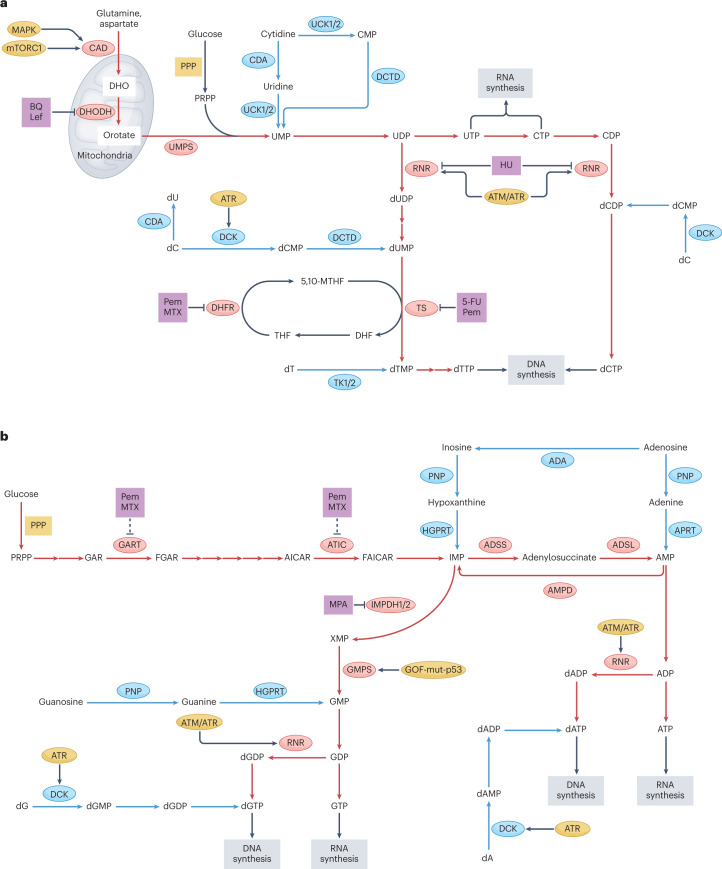
Fig. 1. Biosynthetic pathways for pyrimidine and purine nucleotides, relevant inhibitors and oncogenic regulators.
The biosynthetic pathways leading to pyrimidine (part a) and purine (part b) nucleotides are shown. For both pyrimidines and purines, de novo synthesis entails a complex series of steps that transform amino acids and phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) into uridine monophosphate (UMP) or inosine monophosphate (IMP), respectively; salvage pathways recycle nucleosides and nucleobases to form nucleoside monophosphates (NMPs) or deoxy NMPs in a single step using ATP or PRPP, respectively. The de novo synthesis pathways are shown by red arrows and enzymes, and nucleotide salvage pathways are shown by blue arrows and enzymes. Inhibitors of these pathways are shown in purple boxes. Selected oncogenic regulators that influence these pathways are shown in yellow. In addition to the oncogenic regulators shown, the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) can also be upregulated by the oncogenic factors hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α), mucin 1 (MUC1), MYC and SREBP1. Dashed inhibitory arrows in part b indicate that the inhibitors pemetrexed (Pem) and methotrexate (MTX) inhibit GART and ATIC indirectly by disruption of the folic acid cycle. 5,10-MTHF, 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate; 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil; ADA, adenosine deaminase; ADSL, adenylosuccinate lyase; ADSS, adenylosuccinate synthetase; AICAR, 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-β-d-ribofuranoside; AMPD, AMP deaminase; APRT, adenine phosphoribosyltransferase; BQ, brequinar; CAD, carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II, aspartate transcarbamoylase and dihydroorotase; CDA, cytidine deaminase; CMP, cytidine monophosphate; CTP, cytidine triphosphate; dA, deoxyadenosine; dC, deoxycytidine; dCDP, deoxycytidine phosphate; DCK, deoxycytidine kinase; dCMP, deoxycytidine monophosphate; DCTD, deoxycytidylate deaminase; dCTP, deoxycytidine triphosphate; DHF, dihydrofolate; DHFR, DHF reductase; DHO, dihydroorotate; DHODH, DHO dehydrogenase; dT, thymidine; dTTP, deoxythymidine triphosphate; dU, deoxyuridine; dUMP, deoxyuridine monophosphate; FGAR, phosphoribosyl-N-formylglycineamide; FAICAR, 5-formamidoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribotide; GAR, glycineamide ribonucleotide; GMPS, GMP synthase; GOF-mut-p53, gain-of-function mutant p53; HGPRT, hypoxanthine–guanine phosphoribosyltransferase; HU, hydroxyurea; IMPDH1/2, IMP dehydrogenases 1 and 2; Lef, leflunomide; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MPA, mycophenolic acid; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; PNP, purine nucleoside phosphorylase; RNR, ribonucleotide reductase; THF, tetrahydrofolate; TK1/2, thymidine kinases 1 and 2; TS, thymidylate synthase; UCK1/2, uridine–cytidine kinases 1 and 2; UDP, uridine diphosphate; UMPS, UMP synthase; UTP, uridine triphosphate; XMP, xanthine monophosphate.