Fig. 1.
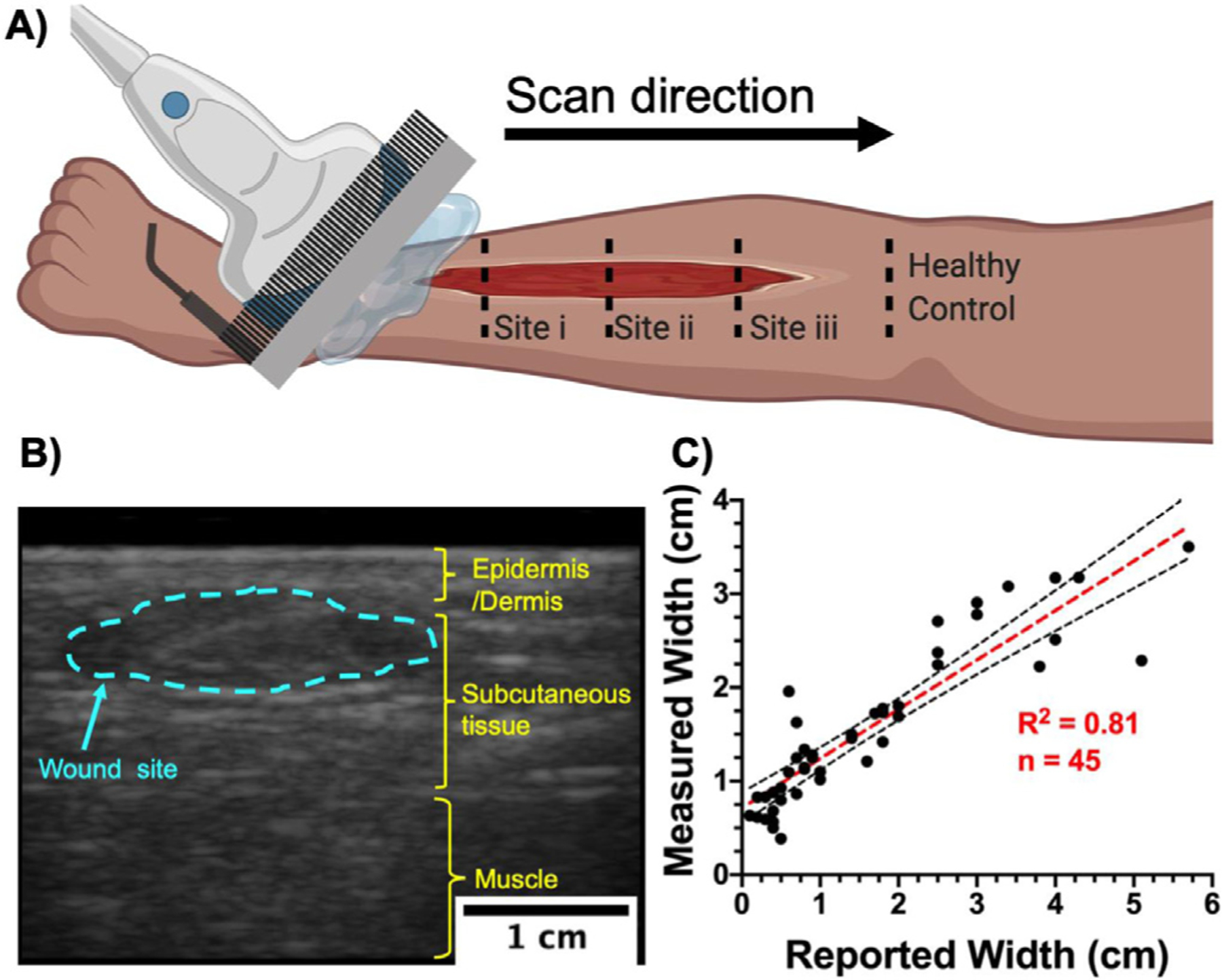
Ultrasound imaging setup and wound width measurement. (a) Schematic representation of a typical ultrasound scan over a wound site. Small wounds (<5 cm in length) were scanned in one sweep from inferior to superior healthy tissue. Large wounds were imaged at discrete distances from the inferior wound edge. Superior and inferior tissue from the wound edge were considered as healthy controls. (b) A typical B-mode US image revealing a coronal cross-section of the lower limb. Wound width was measured at its widest point within the wound site (blue dotted line). (c) Comparison between reported wound width at the point of care and wound width measured using US (n = 45) revealed a strong correlation (R2 = 0.81, p < 0.0001) between the gold standard and our method. Black dotted lines represent 95% confidence intervals.
