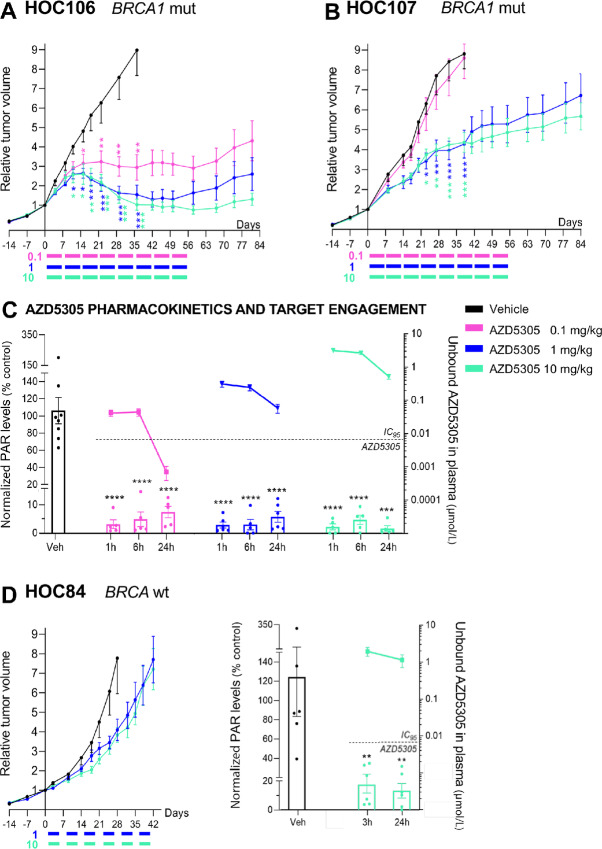
FIGURE 1.
AZD5305 has antitumor activity on subcutaneously growing BRCA1m OC-PDXs. A and B, Relative tumor volume (mean ± SEM) of two BRCA1m OC-PDXs: HOC106 (A) and HOC107 (B). Mice were randomized (stratified randomization) and treated when tumor volume reached 190 mm3 (SD 55.9; A) or 180 mm3 (SD 68.2; B). Colored bars indicate the dosing periods: AZD5305 was given orally at 0.1, 1, or 10 mg/kg every day 5 days ON and two OFF. Treatments lasted 8 weeks. Number of mice/group = 6–7. C, AZD5305 pharmacokinetics and target engagement at 1, 6, and 24 hours after the last of five consecutive treatments administered to HOC107 tumor-bearing mice. Unbound plasma concentrations of AZD5305 (right axis) and total PARylation levels in the tumor lysates (left axis). D,BRCA1wt HOC84 OC-PDX. Left: AZD5305 efficacy. Relative tumor volume (mean ± SEM). Mice were randomized (stratified randomization) and treated when tumor volume reached 170 mm3 (SD 40.8). Colored bars indicate the dosing periods. AZD5305 was given orally at 1 or 10 mg/kg every day 5 days ON and two OFF. Number of mice/group = 7–8. Right: AZD5305 unbound plasma concentrations (right axis) and total PARylation levels in the tumor lysates (left axis) 3 and 24 hours after the last of five consecutive treatments. A–D, Statistical significance versus vehicle treated mice was analyzed as specified in Materials and Methods. *, P < 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.005; ****, P < 0.001.