FIGURE 4.
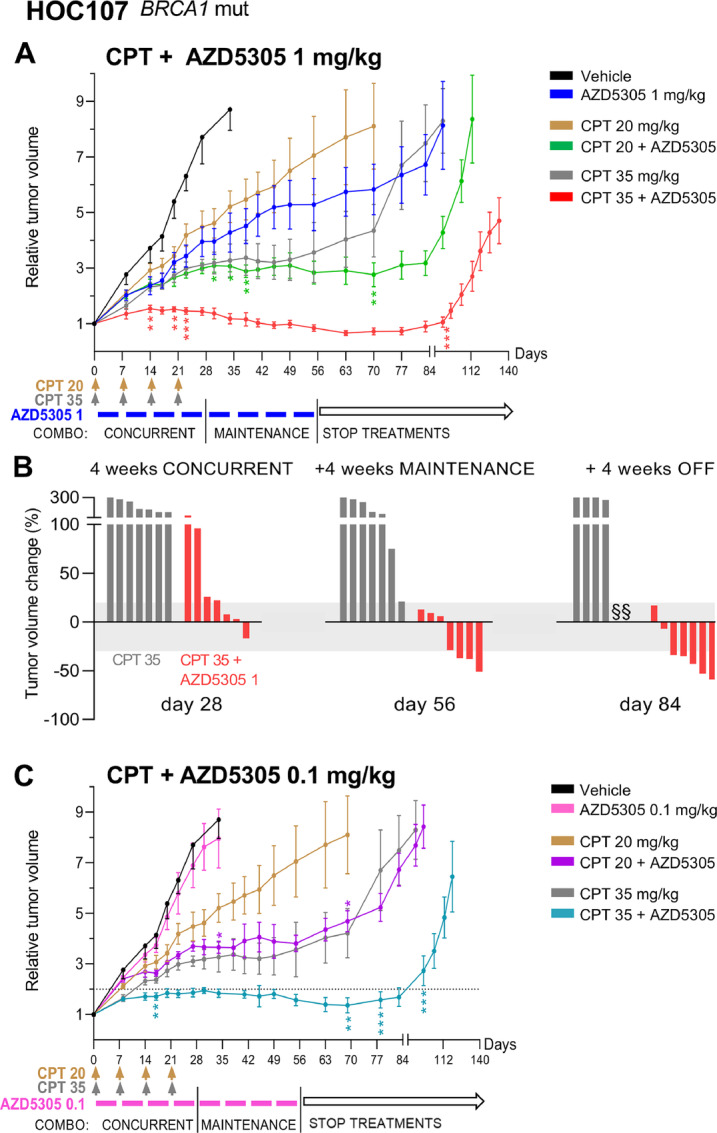
AZD5305 potentiates the effect of CPT, significantly impairing the growth of HOC107 tumors. A, Relative tumor volume (mean ± SEM) of HOC107 tumors growing subcutaneously. Tumor-bearing mice were randomized at a tumor volume of 200 mm3 (SD 67.3) and were treated with CPT (20 or 35 mg/kg i.v., once a week for 4 weeks) and/or AZD5305 1 mg/kg orally every day, 5 days ON and two OFF for 8 weeks, or combination therapy: 4 weeks of concurrent treatment followed by 4 weeks of AZD5305 single agent (maintenance). Colored bars and arrows indicate the dosing periods. Number of mice/group = 6–7. B, Efficacy of the combination CPT plus AZD5305 1 mg/kg expressed as the percentage of change in tumor volume (compared with the volume at treatment start) after 4 weeks of concurrent treatment (day 28), at the end of the therapy (day 56) and 4 weeks after treatment discontinuation (day 84). Each vertical bar in the waterfall plot represents a single mouse/tumor. Stable disease according to RECIST is highlighted in gray (change from +20% to −30%). § Mouse euthanized when the volume considered a predefined endpoint (1,500 mm3) was reached. C, Relative tumor volume (mean ± SEM) of HOC107 tumors growing subcutaneously (vehicle and CPT single agent are the same arms as in A). Tumor-bearing mice were randomized and were treated with CPT (20 or 35 mg/kg) and/or AZD5305 0.1 mg/kg or combination therapy (as described in A). Colored bars and arrows indicate the dosing periods. Number of mice/group = 6–7. Statistical significance of the combination versus matching CPT monotherapy was analyzed as specified in Materials and Methods. *, P < 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.005.
