FIGURE 5.
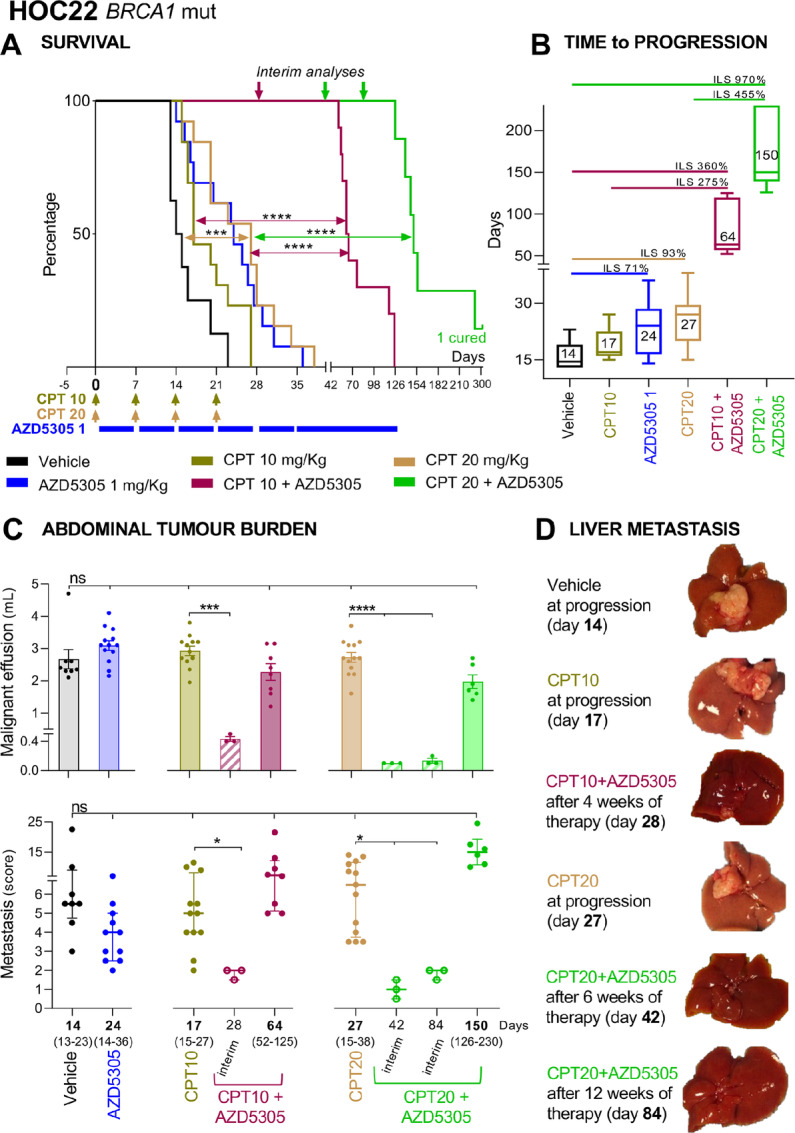
AZD5305 plus CPT significantly impairs the progression of the abdominal disease limiting metastasis and prolonging the lifespan of HOC22 bearing mice. A, Kaplan–Meier curves showing the percentage of survival plotted against time elapsed from treatment start. HOC22 bearing mice were randomized (simple randomization) 5 days after transplantation to receive CPT at 10 or 20 mg/kg (i.v. once a week for 4 weeks) and AZD5305 dosed at 1 mg/kg (orally every day 5 days ON and two OFF, as maintenance regimen) or combination therapy: 4 weeks of concurrent treatment followed by AZD5305 single agent. Colored bars and arrows indicate the dosing. Number of mice/group = 13 (vehicle n = 8). B, Time to progression (TtP). Median with range (days) for each treatment arm; increment of lifespan (ILS%) is also shown. TtP and ILS% were calculated as described in Materials and Methods. C, Abdominal tumor burden. Malignant effusion (top: volume: mean ± SEM) and metastatic dissemination to the peritoneal organs (bottom: median with interquartile range; scattered points are the metastasis scores for each mouse) at time of disease progression (median with range TtP indicated on the X axis) for each treatment arm and at predefined interim times during combination therapy (at days 28, 42, and 84, n = 3). D, Representative images of disseminated livers at time of disease progression (14 days vehicles, 17 days single-agent CPT at 10 mg/kg, and 27 days single-agent CPT at 20 mg/kg) and at predefined interim times during combination therapy, specifically after 4 weeks (day 28) for AZD5305 plus CPT 10 mg/kg, and after 6 and 12 weeks (days 42 and 84) for AZD5305 plus CPT 20 mg/kg. A and C, Statistical significance as specified in Materials and Methods. ns, not significant; *, P < 0.05; ***, P ≤ 0.005; ****, P < 0.001.
