Fig. 2.
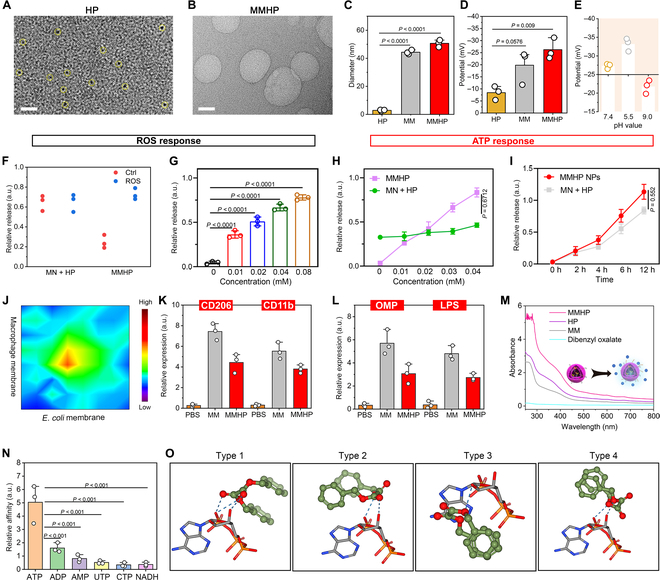
The ROS- and ATP-responsive activity of MMHP NPs. (A) The TEM image of HP. Scale bar, 20 nm. (B) The TEM image of MMHP NPs. Scale bar, 20 nm. (C) The dynamic light scattering size of MM, HP, and MMHP NPs. (D) The zeta potential of MM, HP, and MMHP NPs. (E) The varied zeta potential of MMHP NPs at pH 7.4, 5.5, and 9.0, respectively. (F) The release of HP of MN + HP and MMHP under neutral (Ctrl) or ROS (H2O2) environment. (G) The release of HP in under varied ROS (H2O2) environment from 0.01 to 0.08 mM. (H) The release of HP under different ATP concentrations from 0.01 to 0.04 mM. MN + HP means the physical mixture of MN (mesoporous silicon) and HP. (I) The release of HP under varied time. (J) The release of HP under varied E. coli and macrophage membrane ratio. (K) The CD206 and CD11b protein expressions of PBS, MM, and MMHP NPs. (L) The LPS and OMP protein expression of PBS, MM, and MMHP NPs. (M) The ultraviolet-visible spectra of HP, MM, dibenzyl oxalate, and MMHP NPs from 300 to 800 nm. (N) Varied HP release of MMHPs under ATP and its decomposition product environment. (O) The interaction between ATP and dibenzyl oxalate. (C), (D), (G) to (I), (K), and (L) were analyzed with one-way ANOVA. a.u., arbitrary units.
