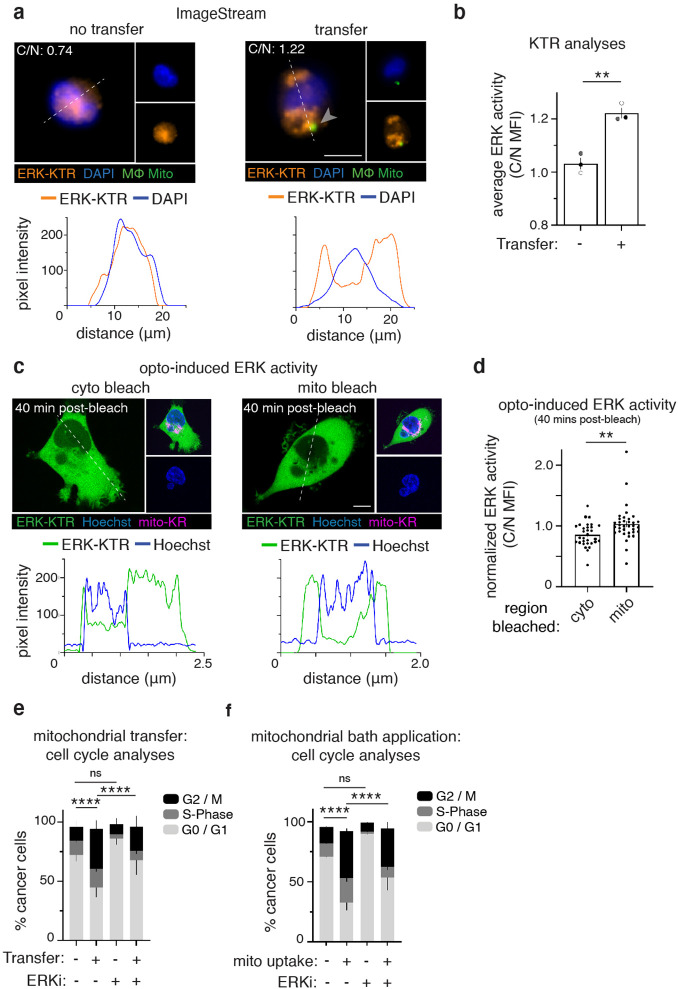
Figure 3. Recipient cancer cells exhibit ERK-dependent proliferation.
(a) ImageStream was used to measure the MFI of an ERK-Kinase Translocation Reporter (ERK-KTR, orange) in the nucleus (DAPI, blue) or cytoplasm of co-cultured 231 cells that did (right) or did not (left) receive mitochondria (green, arrowhead). Below: representative line scans (white dotted lines) of ERK-KTR (orange) and DAPI (blue). (b) Average ERK activity from data displayed in (d) (cytoplasm/nucleus (C/N) mean fluorescence intensity (MFI); N=3 donors indicated as shades of gray). (c) Confocal images of 231 cells expressing ERK-KTR (green) and Mito-KillerRed (magenta) with Hoechst 33342 (blue), after control cytoplasmic bleach (cyto, left) or mito-KillerRed+ bleach (mito, right). Below: representative line scans (white dotted lines) of ERK-KTR (green) and Hoechst (blue). (d) Quantification of ERK-KTR translocation 40 min post-bleach (cyto vs. mito), normalized to time 0. Each dot represents a measurement from a single cell. (e) Analysis of proliferative capacity by quantifying Ki-67 and DNA levels of co-cultured 231 cells treated with vehicle or ERK inhibitor (ERKi) with or without transfer or (f), mitochondrial internalization after mitochondrial bath application (N=3 donors; statistics for G2/M only). Error bars represent SEM and scale bars are 10 µm., Welch’s t-test (b), Mann-Whitney (d), two-way ANOVA (e–f), *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ****p<0.0001.
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Amnis ImageStream pipeline for ERK-KTR quantification.
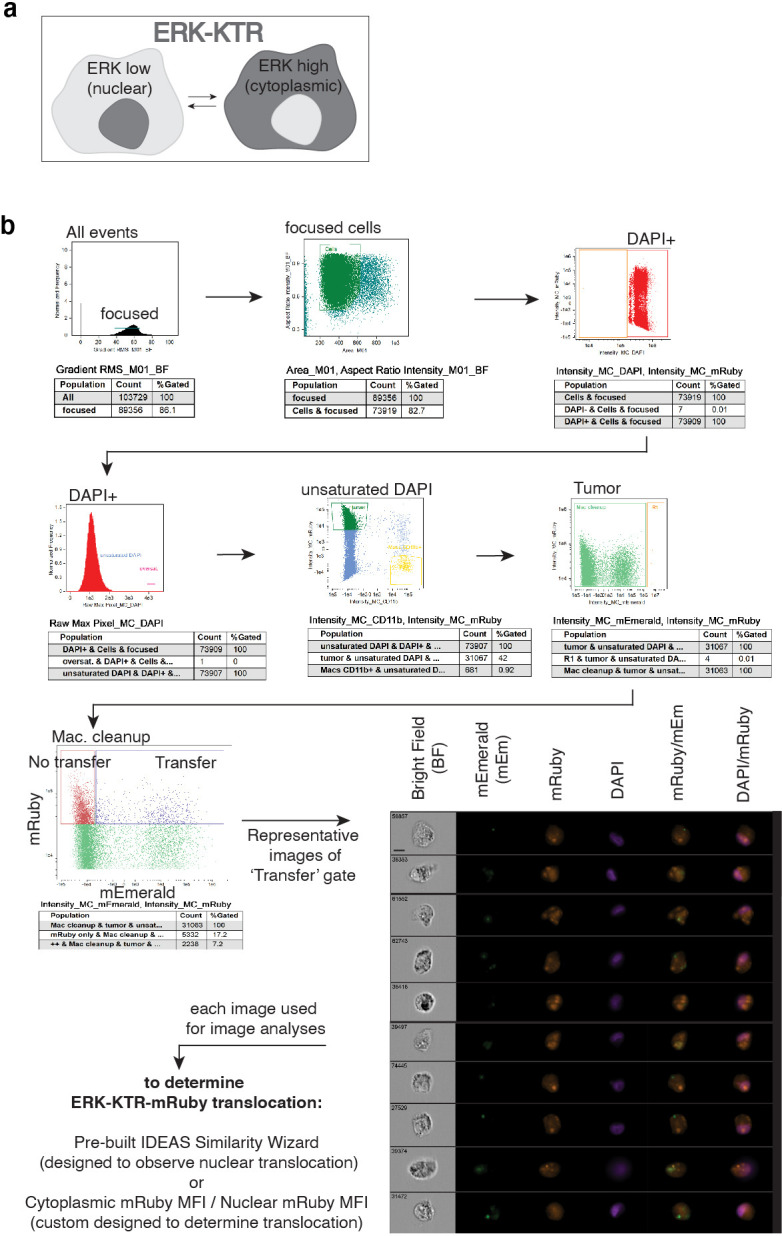
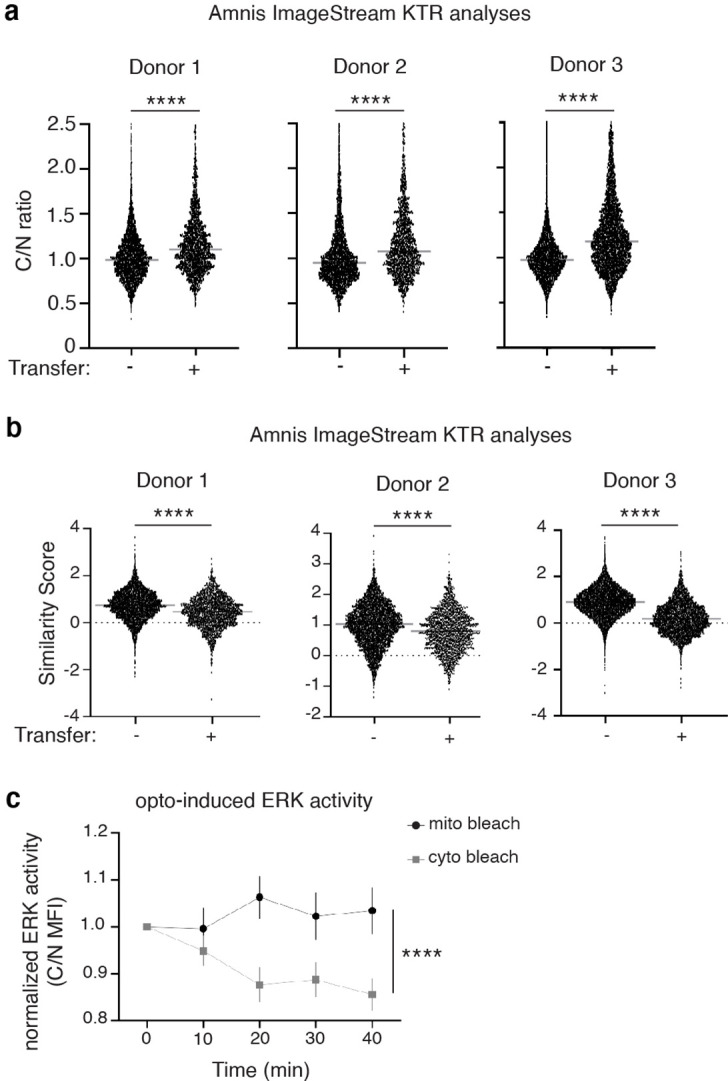
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. ERK-KTR analysis and validation using the Amnis ImageStream pipeline.
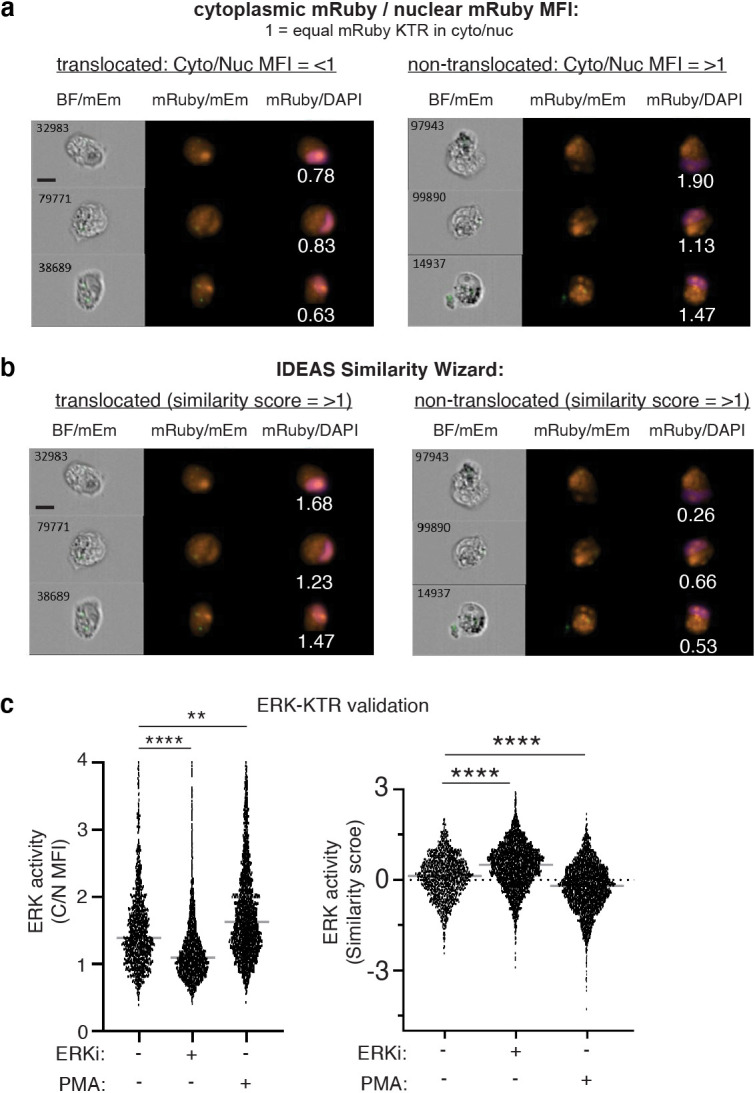
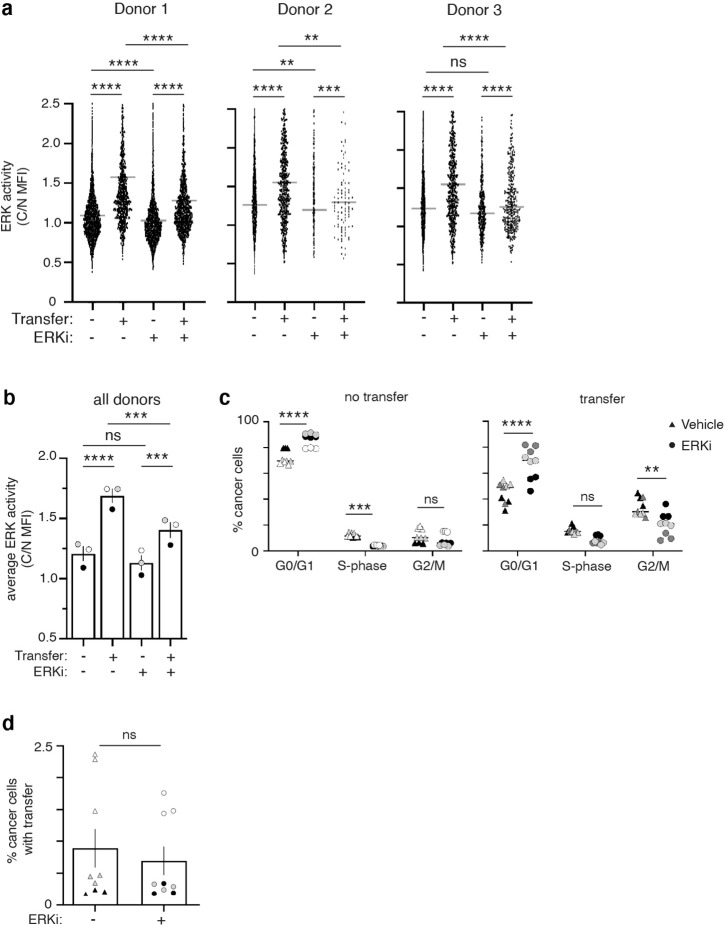
Figure 3—figure supplement 3. Quantification of ERK activity in recipient 231 cells or upon ROS induction.