Fig. 3 |. Nodal facilitation by GABAaxo neurons.
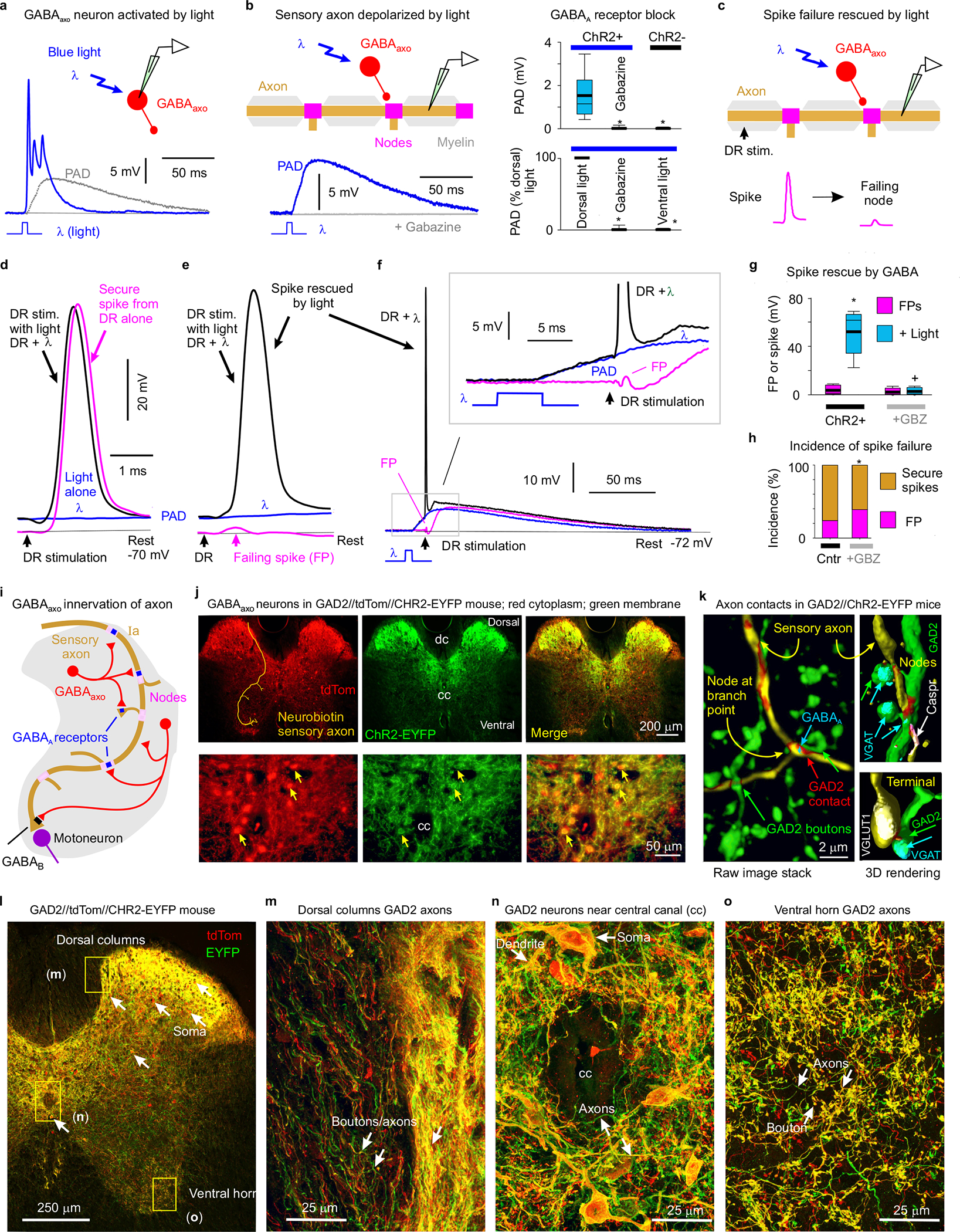
a, Intracellular recording from GABAaxo neuron in ex vivo spinal cord of GAD2//ChR2-EYFP mouse, with ChR2 activated with a light pulse focused on the dorsal horn (5 ms, λ = 447nm laser, 0.7 mW/mm2, 1.5x light threshold to evoke PAD, T) causing a long depolarization and asynchronous spiking (cell isolated in 50 μM gabazine). Average of 10 trials at 0.3 Hz, blue. Cell resting at −61mV. PAD from (b) also shown, grey. b, Intracellular recording from proprioceptive axon branch (in DH, sacral S3, resting at −71 mV; average of 10 trials at 0.3 Hz) with same dorsal light pulse (1.5xT) producing a long depolarization (PAD). Box plots show the interquartile range (box), median (thin line), mean (thick line), extremes, 10 and 90 percentile (whiskers). *significantly less with gabazine or omitting ChR2 (control mice) or focusing light on the ventral rather than dorsal horn (ventral light), two-sided unpaired t-tests with Bonferroni correction, P < 0.05, n = 14 axons each, from 5 mice each. c-g, DR stimulation at rest (1.1xT) evoked a secure spike in some axon branches (d) and not others (e, f, FPs; DH S3 axons). Light evoked PAD (λ, 1.5xT, 10 ms prior) rescued most failed spikes (e, f) and sped up conduction in secure spikes (d). Box plots of FPs and spikes (g); *significant increase with light, two-sided paired t-test, P < 0.05, n = 11 axons from (b); + significant reduction in light effect with 50 μM gabazine or bicuculline, P < 0.05, n =11 axons from (b). h, Incidence of branches with failed DR-evoked spikes. *significant change with gabazine, two-sided χ- squared test, P < 0.05, for n = 45 control axons (Cntr) and n = 27 axons treated with gabazine. i-o, GABAaxo neurons imaged in S3 sacral spinal cord of GAD2//ChR2-EYFP//tdTom mice (j, l-o; green/red, merge yellow; n = 3 mice) or GAD2//ChR2-EYFP mice (k, green, dorsal horn, n = 5 mice). Innervation of neurobiotin filled sensory axons (gold in j and k, as in Fig. 1) by GABAaxo neurons (green; axon contacts labelled red in k) in dorsal horn. Nodes identified by Caspr and paranodal taper, sensory terminals by VGLUT1, GABAaxo terminals by VGAT, and axonal GABAA receptors by the α5GABAA subunit. ChR2-EYFP is mainly expressed on plasma membranes51, whereas tdTom is cytoplasmic (j, l-o). Regions in (l) expanded in (m-o).
