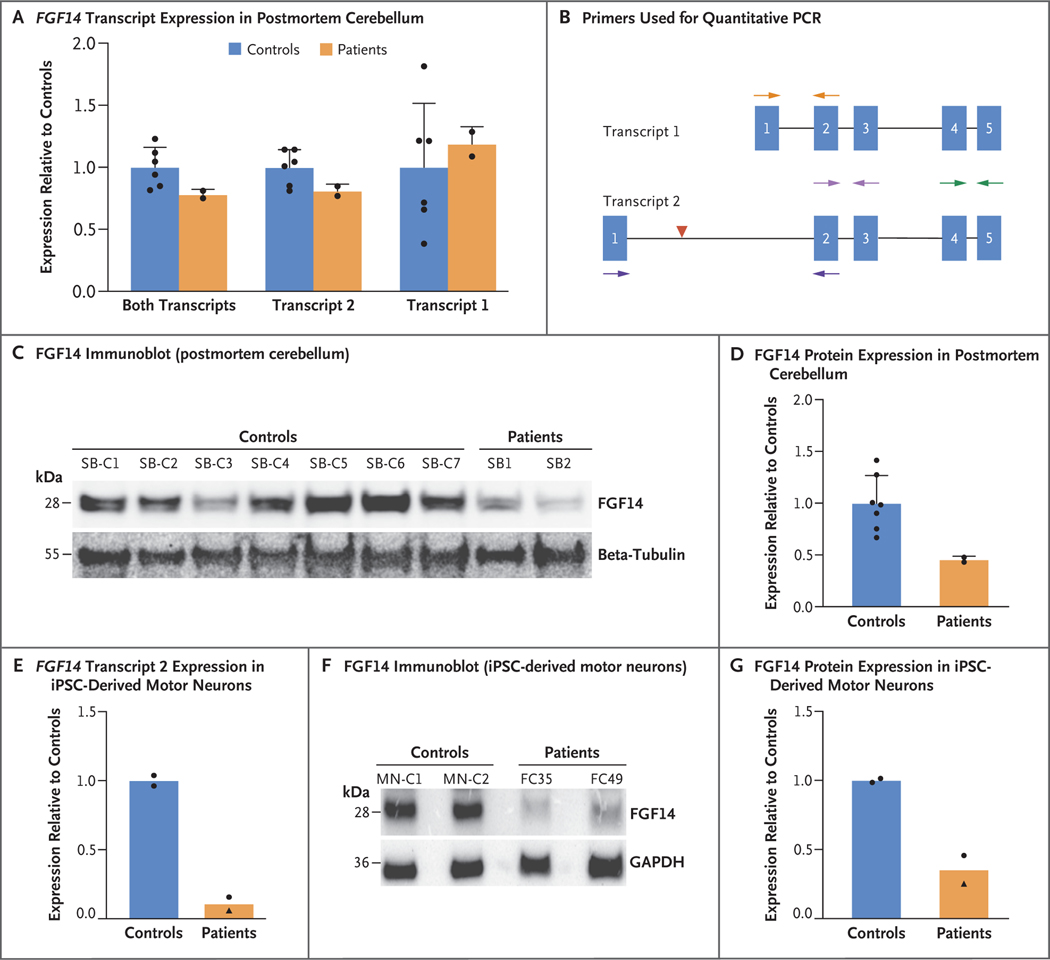
Figure 4. FGF14 Expression and Protein Levels in Cerebellum and iPSC-Derived Motor Neurons.
Panel A shows the relative expression of FGF14 transcript variant 1 (NM_004115.4) and transcript variant 2 (NM_175929.3) mRNA, both together and individually, in the postmortem cerebellar cortex of six controls and two patients, normalized by geometric averaging of the expression of five housekeeping genes (ACTB, HPRT1, YWHAZ, RPL13, and UBE2D2) as assessed by quantitative PCR. Values shown are the ratio of the mean expression relative to the mean among controls. Bars indicate the mean, T bars the standard deviation, and black dots the data distribution. Panel B shows a map of the primers used in quantitative PCR experiments with postmortem cerebellum and induced pluripotent stem-cell (iPSC)–derived motor neurons in relation to the exons of both FGF14 transcripts. Orange arrows indicate the primers used for the transcript 1 assay, dark purple arrows the primers used for the transcript 2 assay, and green arrows and light purple arrows the primers used for total FGF14 expression assays in postmortem cerebellum and iPSC-derived motor neurons, respectively. The position of the GAA repeat expansion in intron 1 of transcript 2 is indicated by a red arrowhead. Panel C shows a representative FGF14 immunoblot of protein extracts from postmortem cerebellar cortex specimens from seven controls and two patients. Beta-tubulin was used as loading control. Western blot analysis was repeated independently three times, with similar results. Panel D shows the mean expression ratios of FGF14 protein in postmortem cerebellar specimens from seven controls and two patients, measured across three independent replicate immunoblots. All ratios were normalized to beta-tubulin and expressed relative to controls. Bars indicate the mean, T bars the standard deviation, and black dots the data distribution. Panel E shows the relative expression of FGF14 transcript 2 in iPSC-derived motor neurons of two controls and two patients, normalized to GAPDH, as assessed by quantitative PCR. Relative quantification was computed by the 2−ΔΔCt method, with the use of the mean value among controls as calibrator; values are represented as the ratio of the mean expression relative to the mean among controls. Bars indicate the mean, and black dots and triangle the data distribution. Panel F shows a representative FGF14 immunoblot of protein extracts from induced motor neurons from two controls and two patients. GAPDH was used as loading control. Western blot analysis was repeated independently twice, with similar results. Panel G shows the mean expression ratios of FGF14 protein in induced motor neurons from two controls and two patients. All ratios were normalized to GAPDH and expressed relative to controls. Bars indicate the mean, and black dots and triangle the data distribution. Black triangles in Panels E and G indicate a patient who was homozygous for (GAA)300 expansions.