Figure 1.
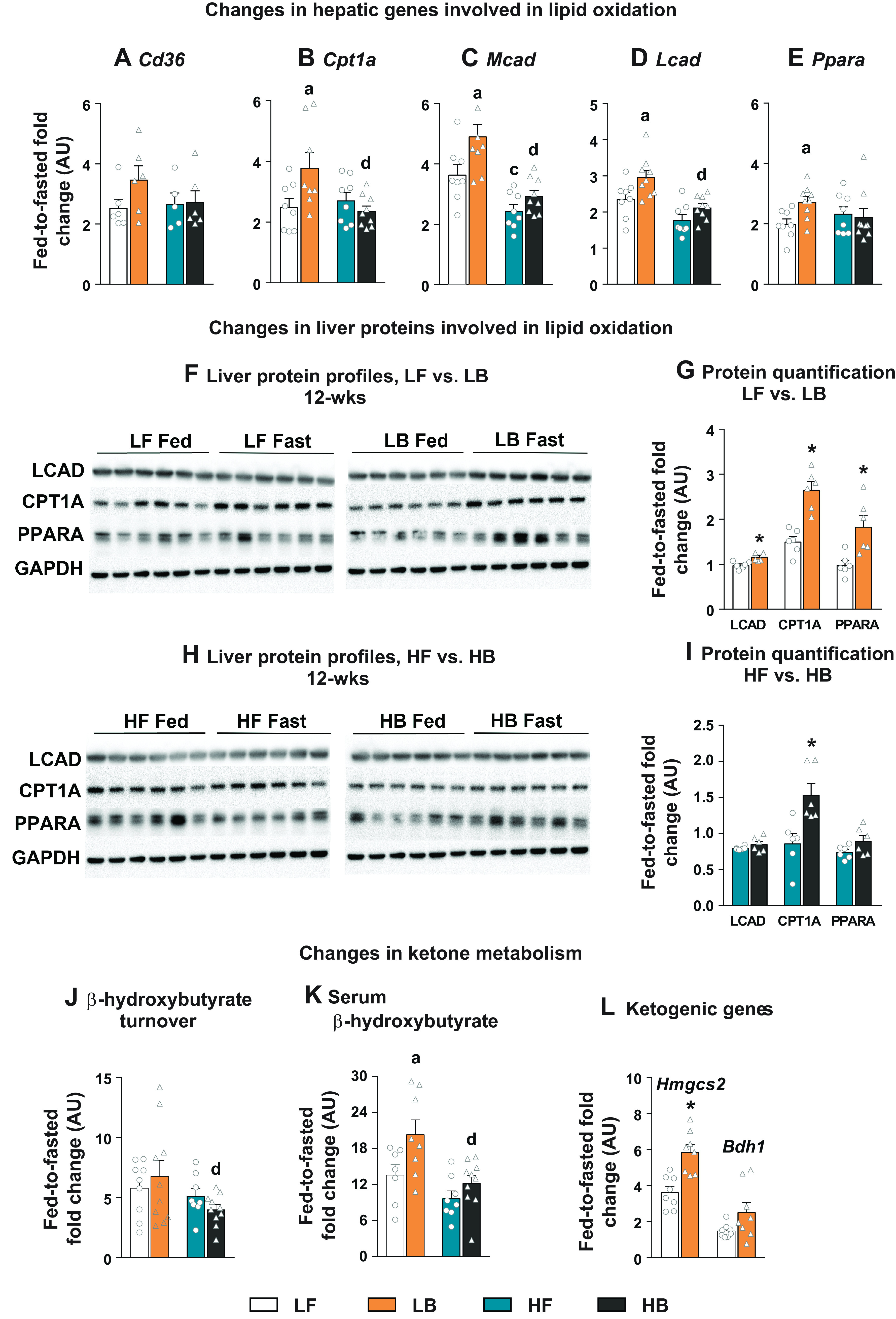
Hepatic lipid oxidation in BCAA-supplemented mice. Fed-to-fasted fold-change in the expression of hepatic genes involved in lipid oxidation including (A) Cd36, (B) Cpt1a, (C) Mcad, (D) Lcad, and (E) Ppara. F: the changes in protein expression of LCAD, CPT1A and PPARA, after 12 wk on LF and LB diets with their densitometry analysis (G). H: the changes in protein expression of LCAD, CPT1A, and PPARA, after 12 wk on HF and HB diets with their densitometry analysis (I). Changes in ketone metabolism: fed-to-fasted fold-changes in the turnover rate of β-hydroxybutyrate (J); fed-to-fasted fold-changes in the circulating levels of β-hydroxybutyrate (K); and fed-to-fasted fold-changes in expression of genes involved in ketogenesis (Hmgcs2 and Bdh1; L). For all the fed-to-fasted comparisons, the normalization is relative to their respective “fed” LF or “fed” HF counterparts. All the values are represented as means ± SE, with n = 5–10/group. Results are considered statistically significant at P ≤ 0.05 following two-way ANOVA followed by pairwise mean comparisons represented as follows: “a”—LF vs. LB; “b”—HF vs. HB; “c”—LF vs. HF; “d”—LB vs. HB. Densitometry analysis between 12-wk (LF vs. LB and HF vs. HB), were determined following a Student’s t test and is represented by “*.” Cd36, cluster of differentiation 36; Cpt1a, carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1; Mcad, medium-chain acyl dehydrogenase; Lcad, long-chain acyl dehydrogenase; Ppara, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α; Hmgcs2, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2 (mitochondrial) and Bdh1; 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase 1; AU, arbitrary units; BCAA, branched-chain amino acid.
