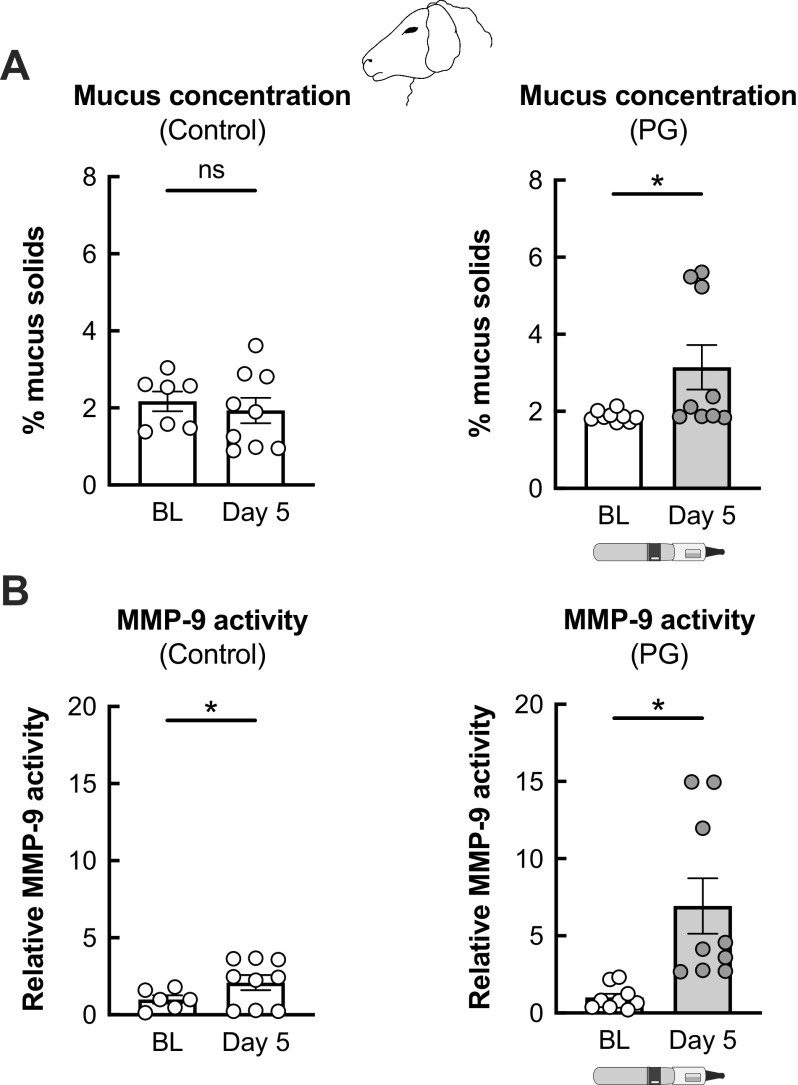
Figure 1.
Airway effects of PG e-cig aerosols in a large animal model (sheep). A: sham-treated, control sheep show no significant changes in mucus concentrations (measured as % mucus solids from tracheal secretions) after 5 days. Five-day exposure of sheep to 100% PG e-cig aerosols causes a significant increase in mucus concentrations. n ≥ 7 from 3 sheep for control. n = 9 from 3 sheep for PG. B: sham-treated, control sheep show an increase in MMP-9 activity measured from tracheal secretions after 5 days, likely due to nasal intubation. Five-day exposure of sheep to PG aerosols causes a significant increase in MMP-9 activity. n ≥ 6 from ≥ 2 sheep for control. n = 9 from 3 sheep for PG. Data are presented as means ± SE. *P < 0.05, ns = not significant. Data were analyzed using a mixed-effects model. PG, propylene glycol.