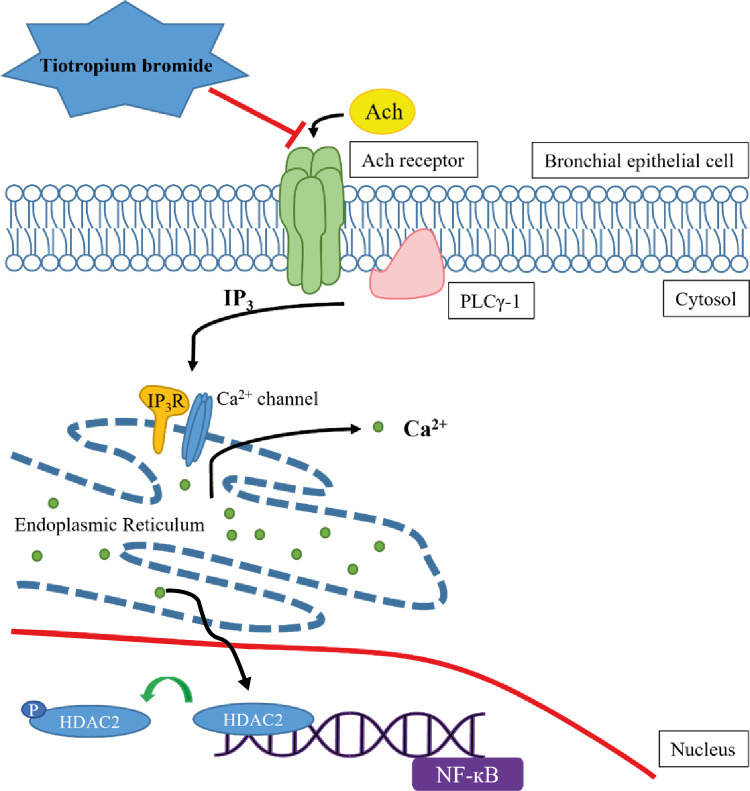
Fig. 6. Proposal of possible mechanism of p-PLCγ-1-IP3-IP3R pathway controlled by TIO in neutrophilic asthma. ACh induces airway inflammation by attaching to its receptor in bronchial epithelial cells. It triggers phosphorylation of PLCγ-1, which leads to an increased level of IP3. It binds to IP3R and IP3-favor calcium channel in the ER. Ionized calcium ions are depleted in the ER. Then, HDAC2 is deactivated by phosphorylation, and NF-κB transcription is triggered in the nucleus. TIO blocks the ACh receptor, which is the highest level of controlling inflammation in neutrophilic asthma. It is mediated by the p-PLCγ-1-IP3-IP3R pathway.
ACh = Acetylcholine, PLCγ-1 = phospholipase Cγ-1, IP3 = inositol trisphosphate, IP3R = inositol trisphosphate receptor, ER = endoplasmic reticulum, HDAC2 = histone deacetylase 2, NF-κB = nuclear factor kappa B, TIO = Tiotropium bromide.