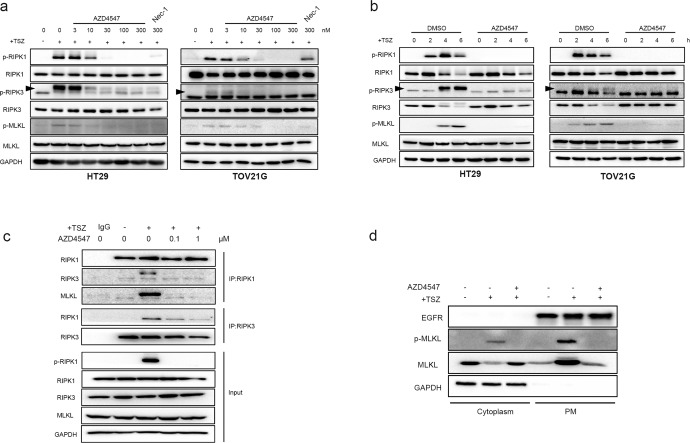
Fig. 5. AZD4547 inhibits necroptosis signaling pathway and blocks necrosome formation.
a HT29 and TOV21G cells were treated with the indicated compound for 1 h prior to the treatment of TSZ for additional 4 h. Cell lysates were harvested and subjected to Western blot analysis for phosphorylation levels of RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL. The arrows indicated the target bands. b The effects of AZD4547 on phosphorylation of RIPK1, RIPK3 and MLKL in TSZ treated HT29 and TOV21G cells. HT29 and TOV21G cells were pretreated with DMSO or 0.5 μM AZD4547 for 1 h, then treated with TSZ for 0, 2, 4 and 6 h. Indicated proteins were detected by immunoblotting. c HT29 cells were treated with the same conditions as Fig. 5a. Cell lysates were co-immunoprecipitated with anti‐RIPK1 or RIPK3 antibody (IP: RIPK1 or RIPK3) and analyzed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. d HT29 cells were treated with AZD4547 for 1 h prior to the treatment of TSZ for additional 6 h. The cells were collected and then separated into cytoplasmic and membrane proteins. The levels of MLKL and p-MLKL were analyzed by Western blotting. GAPDH was used as cytoplasm protein control. EGFR was used as membrane protein control.