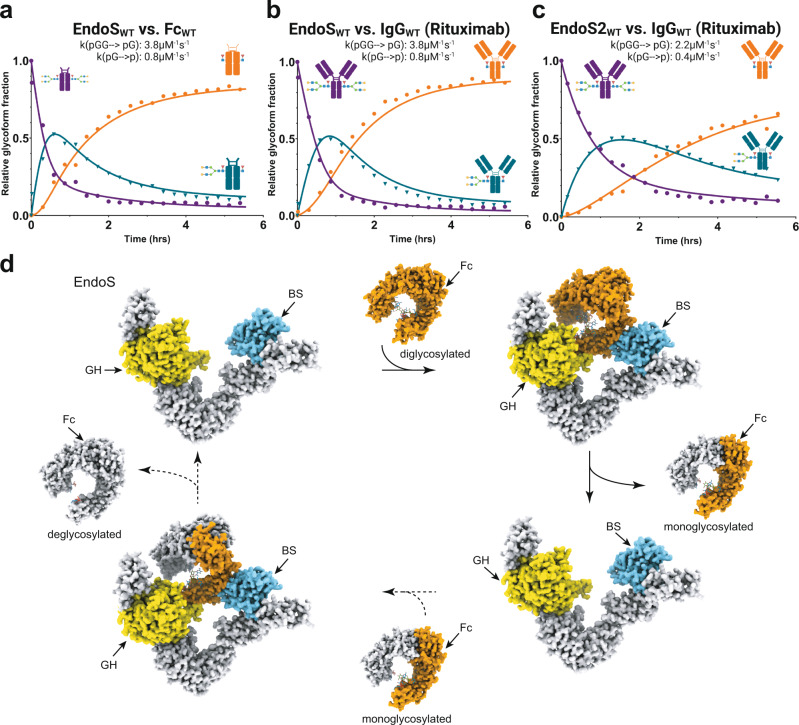
Fig. 5. Molecular mechanism of antibody recognition by EndoS and EndoS2.
Kinetic modeling of deglycosylation of (a) FcWT and (b) IgGWT by EndoSWT and (c) IgGWT by EndoS2WT. LC-MS kinetic analysis of deglycosylation of FcWT and IgGWT by EndoSWT showing the hydrolysis over time of the two N-glycans linked to Asn297. The deglycosylation process occurs sequentially as seen by the initial increase then decrease in monoglycosylated population (dark green) over time while the diglycosylated (purple) and deglycosylated (orange) species increase over time. d Schematic representation of Fc N-glycan processing by EndoS. In a first step, EndoS binds the diglycosylated Fc and hydrolyzes one of the N-glycan of the Fc which causes the release of monoglycosylated Fc. In a second step, EndoS engages the monoglycosylated Fc and hydrolyzes the remaining N-glycan of the Fc to produced completely deglycosylated Fc.