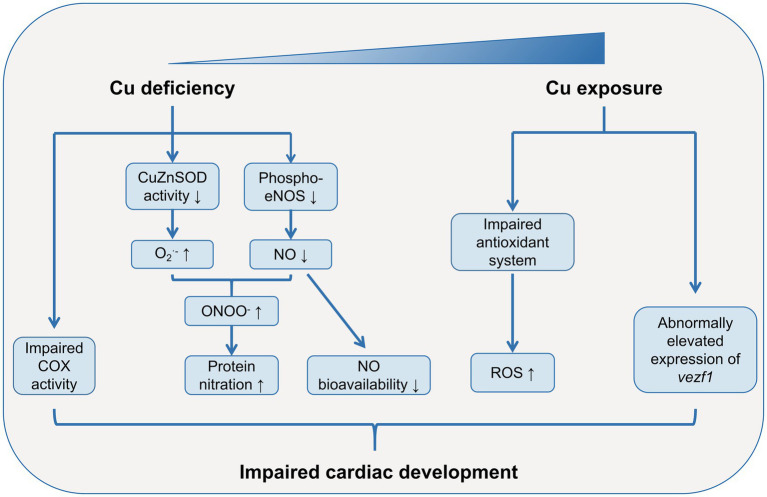
Figure 1.
Role of Cu in cardiac development. Both Cu deficiency and excessive Cu exposure may lead to abnormal cardiac development. Cu deficiency dampens the activity of COX in cardiac mitochondria. Cu deficiency impairs anti-oxidant defense system, resulting in increased ROS levels in embryonic heart. Moreover, the large consumption of NO and decreased phosphorylation levels of eNOS due to Cu deficiency lead to low bioavailability of NO during heart development. Excessive Cu exposure can also impairs anti-oxidant defense system, leading to increased ROS levels in embryonic heart. Cu exposure also alters the expression patterns of development-related gene such as vezf1, which may lead to abnormal cardiac development. COX, cytochrome-c oxidase; Cu, copper; CuZnSOD, Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide (NO) synthase; NO, nitric oxide; ROS, reactive oxygen species; vezf1, vascular endothelial zinc finger 1.