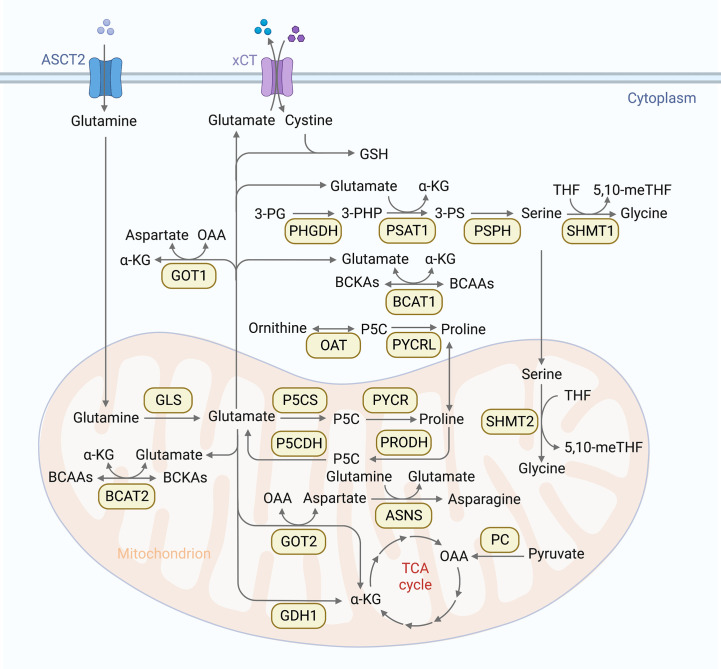
Figure 1.
Overview of amino acid metabolic pathways. Cells absorb glutamine through the glutamine transporter ASCT, then glutamine is converted into glutamate through deamination catalyzed by glutaminase (GLS1/2) in mitochondria. Glutamate is further converted into α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) by glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) in mitochondria. α-KG can promote oxidative TCA cycle and participate α-KG dependent reactions as cofactor. Another TCA supplement way is that pyruvate carboxylase (PC) catalyzes pyruvate into oxaloacetate (OAA). In addition, glutamate and OAA can be reversibly converted into asparagine and α-KG by glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT1/2). Furthermore, glutamate can be secreted by cystine antiporter xCT to transport cystine into cells. Glutamate and cystine can produce glutathione (GSH) to rescue cancer cells from oxidative stress. Glutamine is also involved in serine metabolism. 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PG) is oxidized to 3-phosphate hydroxypyruvate (3-PHP) under the catalysis of phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH), and 3-PHP is catalyzed to 3-phosphoserine (3-PS) by phosphoserine aminotransferase 1(PSAT1), accompanied by the conversion of glutamate to α-KG. 3-PS is then dephosphorylated to serine by phosphoserine phosphatase (PSPH). Serine is reversibly catalyzed by serine-hydroxymethyltransferase 1 (SHMT1) to glycine in cytoplasm, or by SHMT2 in mitochondria. This reaction simultaneously converts tetrahydrofolate (THF) into 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate (5,10 methylene tetrahydrofolate), which is an important source of one carbon (1C) unit. Glutamine is involved in branched chain amino acids (BCAAs) metabolism as well. BCAAs can be catalyzed by BCAA transaminases (BCAT) to reversibly transfer nitrogen to α-KG to generate glutamate and branched chain ketoacid (BCKAs). Glutamine is also involved in proline synthesis. glutamate-γ-Semialdehyde (GSAL) can be synthesized from glutamate by Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase (P5CS) or ornithine by ornithine aminotransferase (OAT), and then generates proline by pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid reductase (PYCR). PYCR can be converted back to Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid (P5C) by proline dehydrogenase/oxidase (PRODH/POX) in mitochondria. P5C can be metabolized to glutamic acid by pyrrolidine-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase (P5CDH) or ornithine by OAT. Glutamine can also be used as a nitrogen donor to participate in the reaction of aspartate to produce endogenous asparagine under the catalysis of asparagine synthetase (ASNS).