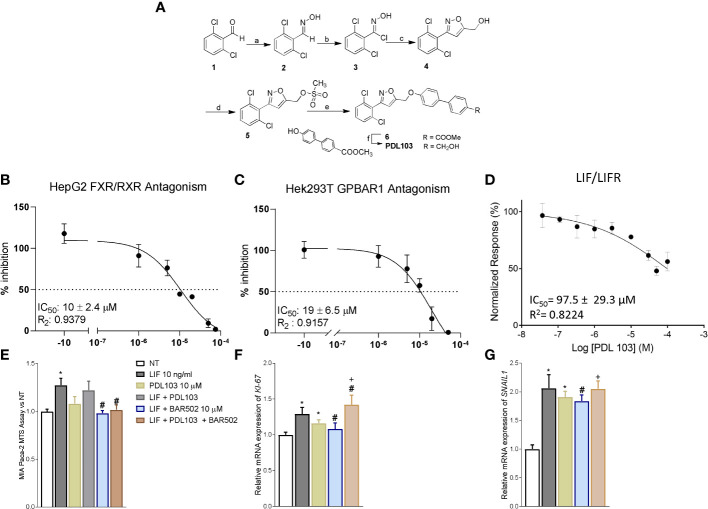
Figure 7.
The effect of BAR502 is mediated through selectively LIFR inhibition. (A) Scheme 1. Reagents and conditions: a) NH2OH·HCl, NaOH, EtOH, Δ, 98%; b) N-clorosuccinimide, dry DMF, 0°C, 95%; c) propargylic alcohol, NaHCO3, CuSO4·5H2O, sodium ascorbate, t-BuOH/H2O 1:1, quantitative yield; d) methanesulfonyl chloride, TEA, dry THF, 92%; e) methyl 4’-hydroxy-4-biphenylcarboxylate, K2CO3, dry DMF, 0°C, 66%; f) LiBH4, MeOH, dry THF, 0°C, 82%. The synthetic strategy was as following: the commercially available 2,6-dichlorobenzaldehyde (1) was treated with hydroxylamine hydrochloride to form the oxime (2) which was in turn chlorinated with NCS to afford the chloro oxime (3). The 3,5-disubstituted isoxazole 4 was easily obtained as only regioisomer via [3 + 2]-cycloaddition between the 2,6-dichloro-N-hydroxybenzimidoyl chloride (3) and propargyl alcohol in presence of NaHCO3, catalytic CuSO4·5H2O and sodium ascorbate with quantitative yield. The intermediate 4 was then reacted with mesyl chloride and triethylamine to afford the mesyl ester (5) which was in turn coupled to methyl 4’-hydroxy-4-biphenylcarboxylate to afford the methyl esters 6. Finally, reduction with LiBH4 gave PDL103. (B, C) Antagonistic effects of PDL103 on FXR and GPBAR1 transactivation induced by CDCA and LCA, respectively, in HepG2 cells. (D) PDL103 inhibition activity of LIFR/LIF binding accessed by a cell-free AlphaScreen assay. (E) MTS assay performed on MIA PaCa-2. Each value is expressed relative to the non-treated (NT) value, which is arbitrarily set to 1. Results are the mean ± SEM of 10 samples per group. Relative mRNA expression of the proliferative marker (* represents statistical significance versus NT; # versus LIF; + versus PDL103) (F) KI-67 and (G) the EMT marker SNAIL1. Each value is normalized to GAPDH and is expressed relative to those of positive controls, which are arbitrarily set to 1. Results are the mean ± SEM of 5 samples per group.