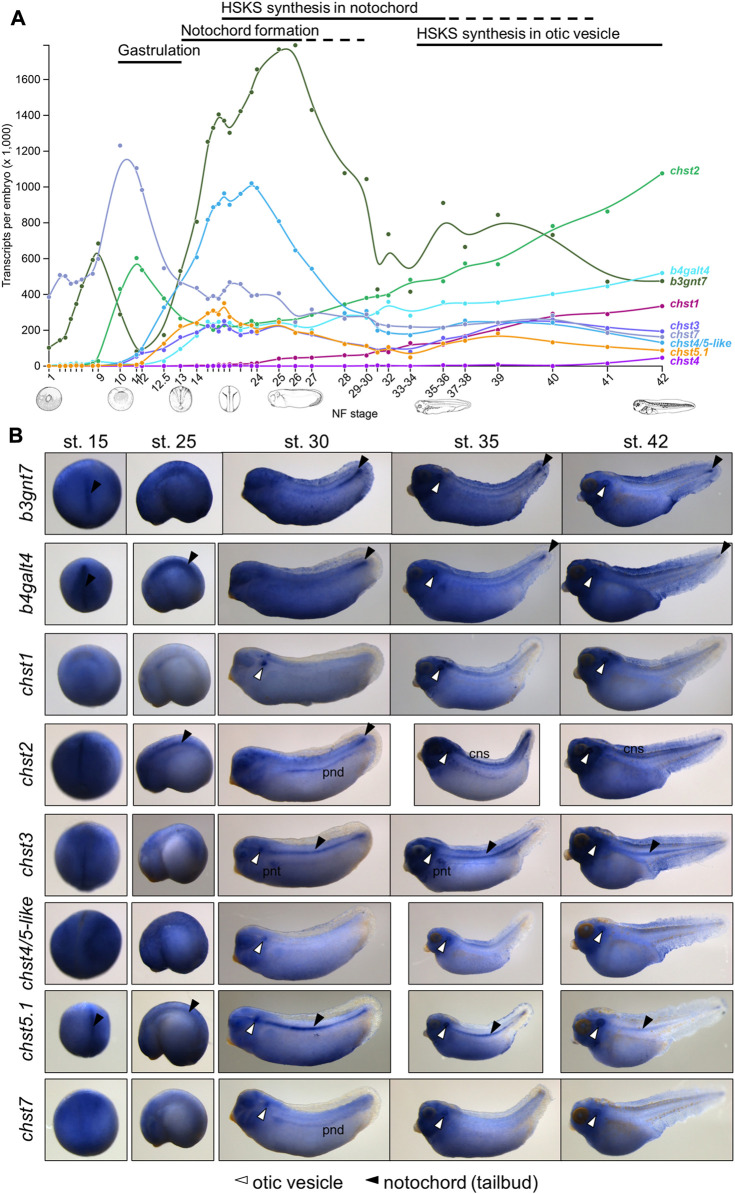
FIGURE 2.
Spatio-temporal expression patterns of HSKS catalytic genes are linked to HSKS synthesis during Xenopus development (A) Expression levels of HSKS biosynthetic genes along the developmental time-course of Xenopus embryos are visualized in Xenbase (https://www.xenbase.org/) using an available RNA-seq dataset (Owens et al., 2016). Most genes showed elevation of expression levels corresponding to enrichment of HSKS in the notochord and otic vesicles. (B) Spatial expression patterns of Xenopus HSKS biosynthetic genes are represented with whole mount in situ hybridization from neurula to tadpole stages (st. 15–42). To detect their expression in the notochord, some embryos were overstained, resulting in higher background, especially in the head region of tadpoles. Therefore, it is difficult to distinguish precise expression domains of genes strongly expressed in the brain such as chst1, chst2, and chst3. Arrowhead, notochord; open arrowhead, otic vesicles; cns, central nervous system; pnd, pronephric duct; pnt, pronephric tubules.