Fig. 6.
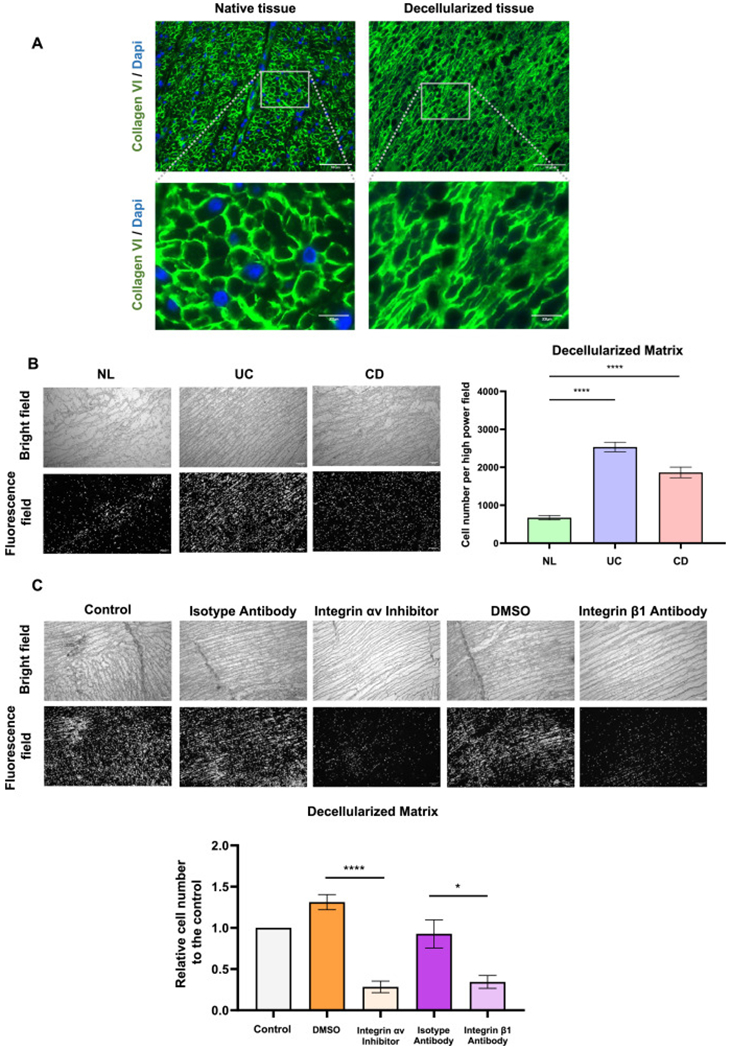
T cell adhesiveness of inflammatory bowel disease decellularized tissue is inhibited by the blockage of integrin αv or integrin β1 in decellularized intestinal matrix
(A) Immunofluorescence staining showing successful removal of cellular components of the decellularized intestinal tissue as indicated by nuclear DAPI stain with extracellular matrix (ECM) structure and collagen VI amount remaining intact. (B) A higher amount of T cells adhered to ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD) decellularized intestinal tissue sections compared to normal control (NL) tissues (n = 6, t test). (C) The adhesiveness of T cells to decellularized tissue dramatically decreased by the blockage of integrin αv or integrin β1 (n = 6, t test). *, p < 0.05, ****, p < 0.0001.
