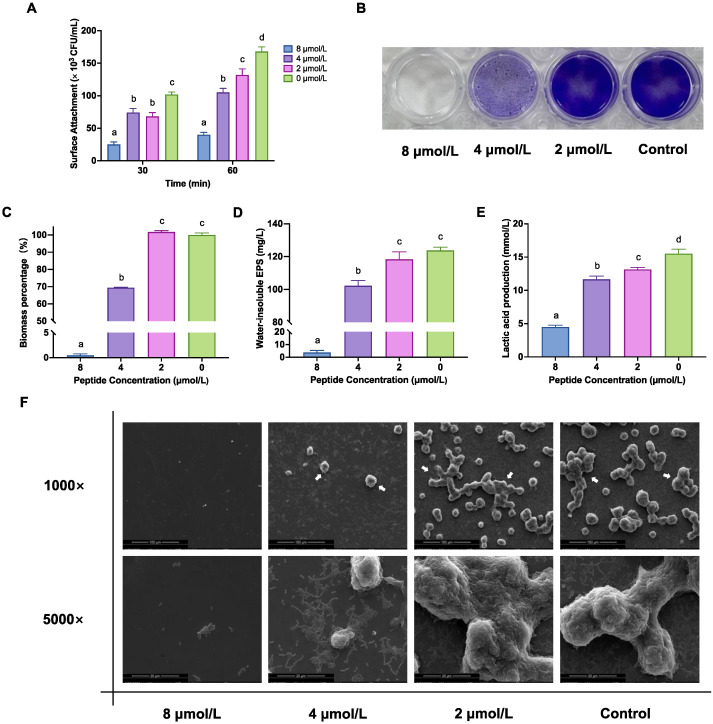
Figure 2.
The inhibition of LF-1 on the adhesion and biofilm formation of Streptococcus mutans. LF-1 significantly decreases the surface-attached S. mutans in a concentration-dependent manner. (A) The inhibition of LF-1 on S. mutans biofilm formation is visually presented by the representative images of CV-stained biofilms (B) and assessed by measuring the biomass percentage (C), water-insoluble EPS (D), and lactic acid production. (E) SEM observations (F) further confirm that LF-1 alters the ultrastructural morphology of the S. mutans biofilm with visually reduced extracellular matrix and bacteria. The arrows indicate the bacterial clusters that comprise aggregated S. mutans wrapped in EPS. All data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation from at least three independent experiments, and relative values are obtained by comparison with the untreated control. Columns labelled with different superscript letters denote significant statistical differences in one group (one- or two-way analysis of variance; p < 0.05). CV: crystal violet; EPS: exopolysaccharide; SEM: scanning electron microscopy.