Abstract
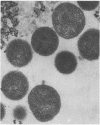
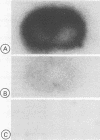
Persistent infectious polyarthritis caused by Ureaplasma urealyticum in a patient with common variable hypogammaglobulinaemia is described. The patient developed a symmetrical, destructive polyarthritis and tenosynovitis associated with a markedly depressed synovial fluid glucose concentration and characteristic soft tissue abscesses. The ureaplasma organism developed resistance to multiple antibiotics and persisted for five years. The organism was identified repeatedly in many joints by culture, confirmed by DNA hybridisation, and mycoplasma-like structures were shown in synovial tissues by electron microscopy.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cassell G. H., Cole B. C. Mycoplasmas as agents of human disease. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jan 8;304(2):80–89. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198101083040204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göbel U. B., Stanbridge E. J. Cloned mycoplasma ribosomal RNA genes for the detection of mycoplasma contamination in tissue cultures. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1211–1213. doi: 10.1126/science.6505688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez L. A., Urquhart G. E., Dick W. C. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection and arthritis in man. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):14–16. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston C. L., Webster A. D., Taylor-Robinson D., Rapaport G., Hughes G. R. Primary late-onset hypogammaglobulinaemia associated with inflammatory polyarthritis and septic arthritis due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Feb;42(1):108–110. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.1.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus V. B., Baraniuk J. N., Hill G. B., Allen N. B. Ureaplasma urealyticum septic arthritis in hypogammaglobulinemia. J Rheumatol. 1988 Feb;15(2):369–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. A. Bromothymol blue broth: improved medium for detection of Ureaplasma urealyticum (T-strain mycoplasma). J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):127–132. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.127-132.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. A., Coppola J. E., Heisler O. R. Standardized method for determining antimicrobial susceptibility of strains of Ureaplasma urealyticum and their response to tetracycline, erythromycin, and rosaramicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):53–58. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. A., Stemke G. W., Maclellan S. G., Taylor D. E. Characterization of tetracycline-resistant strains of Ureaplasma urealyticum. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Mar;21(3):319–332. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So A. K., Furr P. M., Taylor-Robinson D., Webster A. D. Arthritis caused by Mycoplasma salivarium in hypogammaglobulinaemia. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Mar 5;286(6367):762–763. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6367.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemke G. W., Robertson J. A. Modified colony indirect epifluorescence test for serotyping Ureaplasma urealyticum and an adaptation to detect common antigenic specificity. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Nov;14(5):582–584. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.5.582-584.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuckey M., Quinn P. A., Gelfand E. W. Identification of Ureaplasma urealyticum (T-strain Mycoplasma) in patient with polyarthritis. Lancet. 1978 Oct 28;2(8096):917–920. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91632-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Furr P. M., Webster A. D. Ureaplasma urealyticum causing persistent urethritis in a patient with hypogammaglobulinaemia. Genitourin Med. 1985 Dec;61(6):404–408. doi: 10.1136/sti.61.6.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Furr P. M., Webster A. D. Ureaplasma urealyticum in the immunocompromised host. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;5(6 Suppl):S236–S238. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198611010-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Gumpel J. M., Hill A., Swannell A. J. Isolation of Mycoplasma pneumoniae from the synovial fluid of a hypogrammaglobulinaemic patient in a survey of patients with inflammatory polyarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1978 Apr;37(2):180–182. doi: 10.1136/ard.37.2.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogler L. B., Waites K. B., Wright P. F., Perrin J. M., Cassell G. H. Ureaplasma urealyticum polyarthritis in agammaglobulinemia. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1985 Nov-Dec;4(6):687–691. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198511000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster A. D., Loewi G., Dourmashkin R. D., Golding D. N., Ward D. J., Asherson G. L. Polyarthritis in adults with hypogammaglobulinaemia and its rapid response to immunoglobulin treatment. Br Med J. 1976 May 29;1(6021):1314–1316. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6021.1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster A. D., Taylor-Robinson D., Furr P. M., Asherson G. L. Mycoplasmal (ureaplasma) septic arthritis in hypogammaglobulinaemia. Br Med J. 1978 Feb 25;1(6111):478–479. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6111.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]