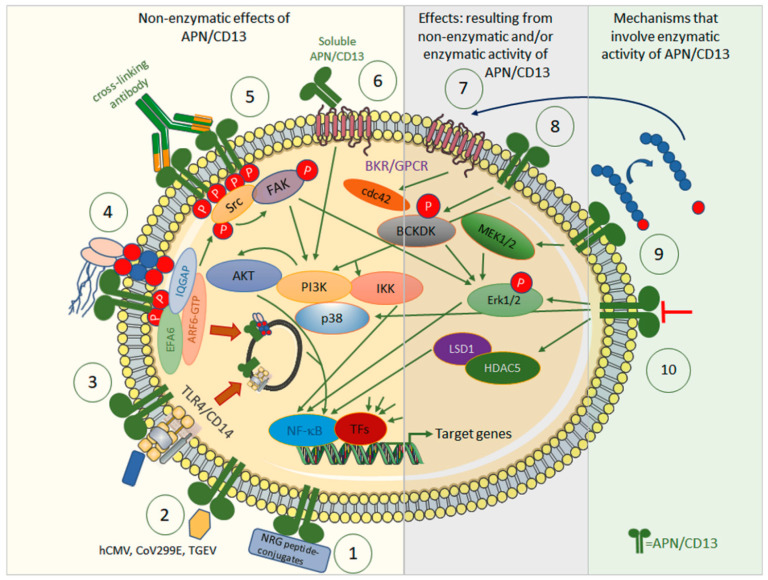
Figure 1.
Effects of APN/CD13 by means of its enzymatic activity (right) or independently of it (left), and the signal transduction pathways involved. Non-enzymatic: ① APN/CD13 allows tumor-specific drug targeting, with, e.g., NRG-peptide conjugates, against APN/CD13-positive tumors or associated cells. ② APN/CD13 serves as a receptor for certain human and porcine viruses, such as CoV229E, hCMV, and TGEV. ③ APN/CD13 regulates internalization of TLR4 and downstream innate signaling cascades via NF-κB and endosomal signaling via IRF-3. ④ In wild-type cells, APN/CD13 is internalized together with integrins and IQGAP-1 into early endosomes, sorted into recycling endosomes, and returned to the cell surface. Lack of APN/CD13 leads to transfer to lysosomes and degradation of integrin instead. Cross-linking of APN/CD13 leads to its clustering and tyrosine phosphorylation with subsequent activation of FAK and ERK kinases. APN/CD13 also tethers the IQGAP1-ARF6-EFA6 complex to the plasma membrane to promote ARF6 activation, β1 integrin recycling, and cell migration. ⑤ Cross-linking antibodies induce the clustering of CD13, tyrosine phosphorylation of CD13, and activation/phosphorylation of Src kinase, which in turn activates/phosphorylates both FAK and ERK kinases, and other components of the MAPK and PI3K pathways. ⑥ Strong chemoattractant, angiogenic, and arthritogenic activity has been attributed to soluble APN/CD13. Soluble APN/CD13 binds to bradykinin receptor 1 (B1R), which is highly expressed in, e.g., synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. ⑦ APN/CD13 controls access of bradykinin to its bradykinin 2 receptor to induce small GTPase cdc42 signaling, filipodia formation, and thus, migration. ⑧ APN/CD3 mediate phosphorylation at serine 31 of branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase kinase (BCKDK) to promote its interaction with and the activation/phosphorylation of ERK1/2. Enzymatic activity involved: ⑨ APN/CD13 regulates availability and/or receptor specificity of various bioactive peptides. These may contribute to altered cellular signaling via their specific receptors, e.g., B2R. ⑩ Inhibitors and (partially) inhibiting antibodies against APN/CD13 have been shown to influence, e.g., angiogenesis and migration. APN/CD13 binds to and stabilizes HDAC5. Inhibition or lack of APN/CD13 destabilizes HDAC5. APN/CD13 may also signal via p38 MAPK.