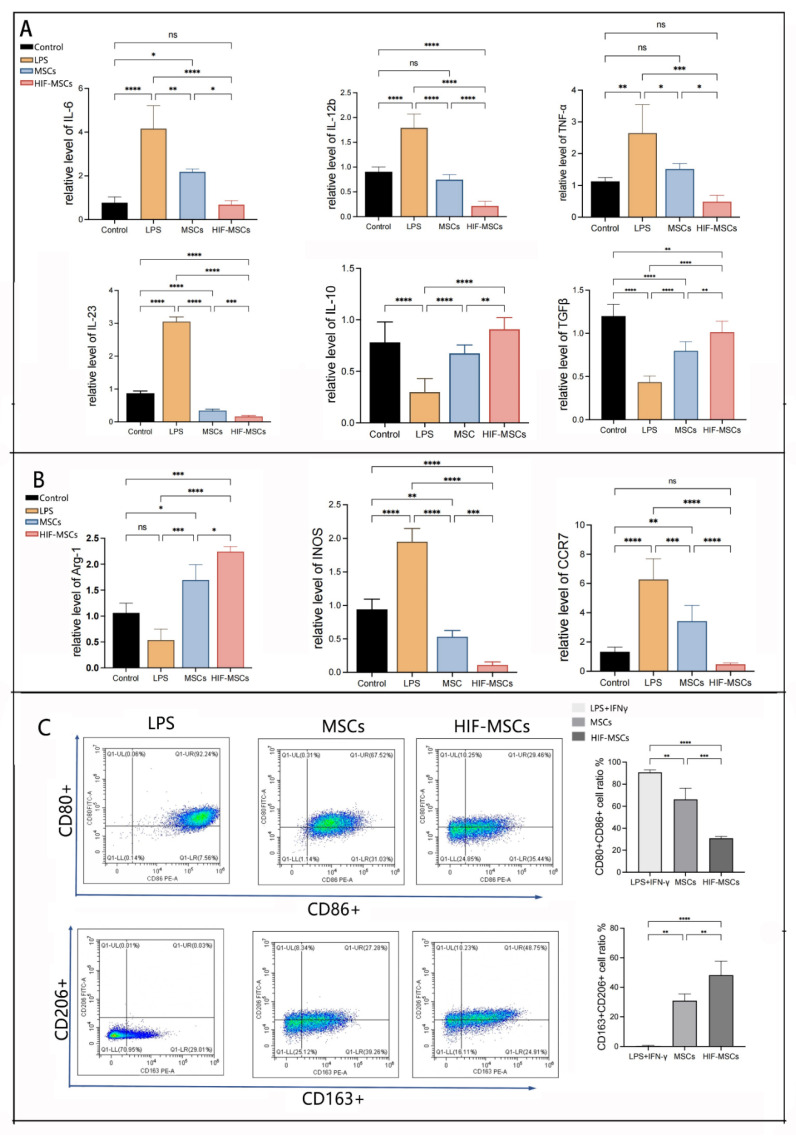
Figure 5.
In vitro, PMA- and LPS/IFN-γ-induced M1-like macrophages were used as the cellular inflammation model, co-cultured with MSCs and HIF-MSCs for 48 h. qPCR was used to detect relative target gene expression in cells. (A). HIF-MSCs promoted anti-inflammatory cytokine expression and inhibited pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in M1 macrophages (**** p < 0.0001, *** p < 0.001). The difference in inflammatory cytokines expression was significant between HIF-MSCs and MSCs (**** p < 0.0001, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05). (B). HIF-MSCs co-culturing effectively upregulated Arg-1 expression and downregulated INOS and CCR-7 expression in M1 macrophages (**** p < 0.0001, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05). (C). Collected macrophages were labeled with anti-CD80, anti-CD86, anti-CD163, and anti-CD206 antibodies, then analyzed via flow cytometry in three independent experiments. M1-like macrophages were gated as double-positive CD 80+CD86+, and M2-like macrophages were gated as double-positive CD163+CD206. HIF-MSCs decreased the M1-like macrophage ratio and increased the M2-like macrophage ratio compared with those in the LPS and MSC groups (**** p < 0.0001, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01). “ns” represented no significant difference.