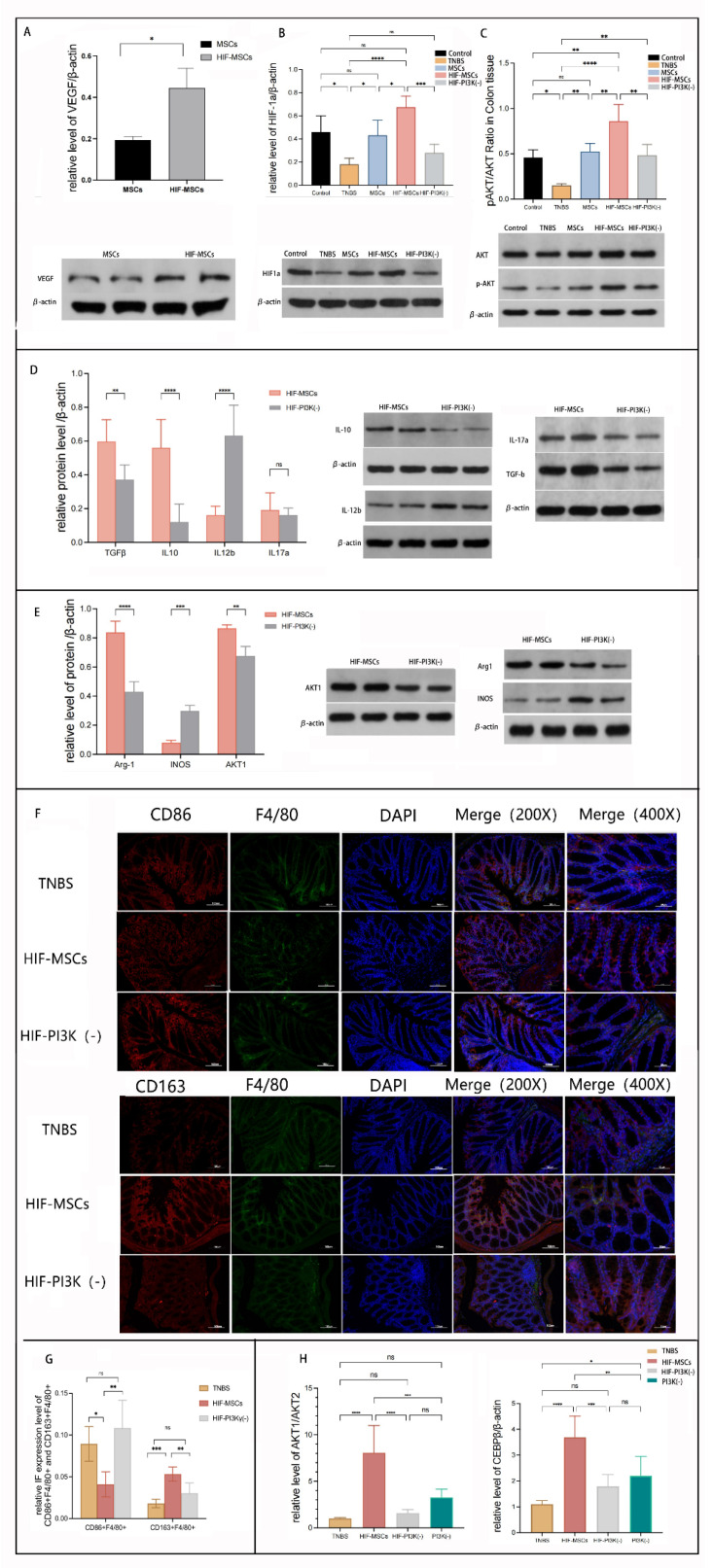
Figure 6.
HIF-MSCs affected macrophage polarization through the PI3K-γ pathway. IPI549 was used to block the PI3K-γ pathway in mice and in induced M1-like macrophages. (A). Western blotting was used to detect VEGF in HIF-MSCs and MSCs. VEGF had a significantly higher expression in HIF-MSCs (*p < 0.05). (B,C). HIF-MSC treatment upregulated the expression of HIF-1α and p-AKT/AKT when compared with those of MSCs and PBS (**** p < 0.0001, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05). PI3K-γ inhibition blocked the up-regulatory effect of HIF-MSCs on HIF-1α and p-AKT/AKT (*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01). (D). PI3K-γ inhibition attenuated the regulatory effect of HIF-MSCs on inflammatory factors; there was a significant difference in IL-12b, TGF-β, and IL-10 expression between the HIF- MSC group and the HIF-MSC–PI3K-γ inhibition group (**** p < 0.0001, ** p < 0.01). (E). PI3K-γ inhibition decreased the expression of Arg-1 and AKT1 and increased that of INOS (**** p < 0.0001, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01). (F,G). PI3K-γ inhibition decreased the relative expression ratio of F4/80+CD163+ and increased the relative expression ratio of F4/80+CD86+ (*** p < 0.001, ** p< 0.01, * p < 0.05) in colonic tissue compared with the HIF-MSC group (H). qPCR was used to detect AKT1, AKT2, and C/EBPβ expression in macrophages. HIF-MSCs had upregulated AKT1/AKT2 and C/EBPβ expression; the effect was significantly blocked upon PI3K-γ initiation treatment (**** p < 0.0001, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05). “ns” represent no significant difference.