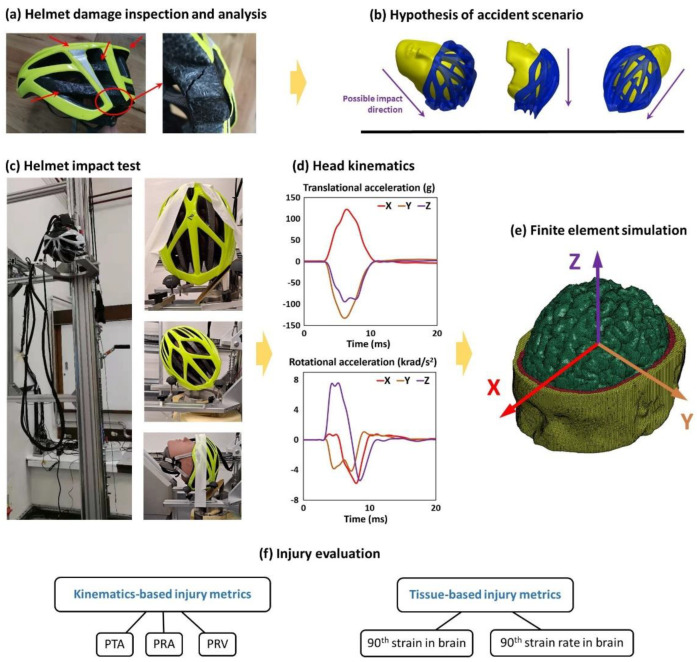
Figure 1.
(a) The cyclist’s helmet was firstly inspected and all damages were analysed. (b) We then hypothesised the accident scenario including the head trajectory and range of head impact speed and direction. (c) Next, we placed the helmeted headform onto a U-shaped platform, which was raised to a certain height to generate a desired impact speed from free fall. The headform’s orientation and the impact speed were chosen based on the hypothesised accident scenarios. (d) For each test, three translational and three rotational acceleration time-history data were recorded with the HIII headform. (e) These acceleration data were then applied to a detailed finite element model of human head to determine the brain strain and strain rate. (f) Finally, we evaluate the brain injury using two types of injury metrics: kinematics-based injury metrics and tissue-based injury metrics.