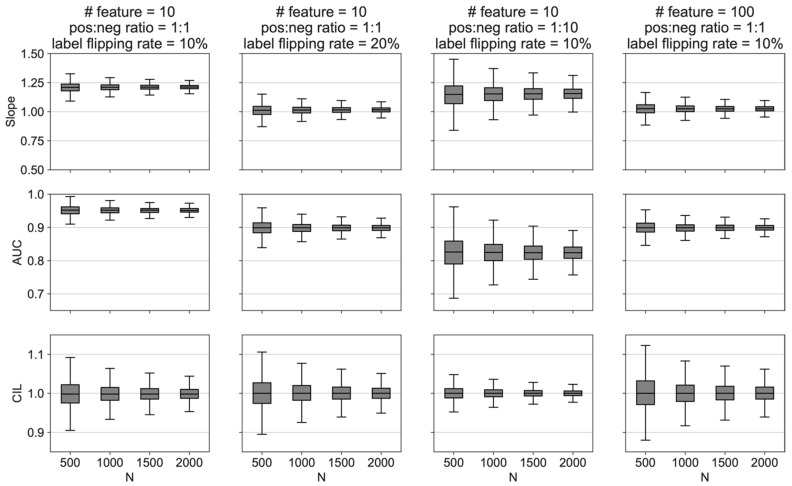
Figure 2.
We generated four simulated datasets (in four columns) representing a binary classification problem that have different numbers (#) of features (10 and 100), positive vs. negative class imbalance ratios (1:1 and 1:10), and noise levels (label flipping rate of 10% and 20%). Each dataset was fit using a logistic regression. The fitted data were then fed into the SSAML algorithm. The purpose is to explore the behavior of the confidence intervals of the calibration slope (top row), AUC (middle row), and CIL (bottom row) under known conditions. Several simple observations can be made here: (1) the confidence intervals decreased with increasing N in all conditions; (2) the calibration slope was sensitive to different conditions; (3) increased noisy or class imbalance decreased the AUC; (4) CIL was not sensitive to the different conditions tested; and (5) evaluating all three metrics (slope, AUC, and CIL) was important.