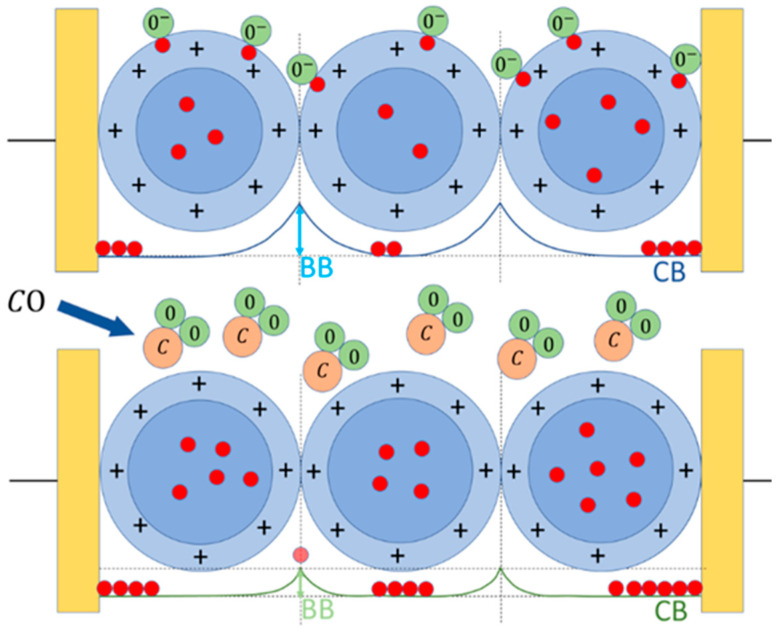
Figure 2.
Working principle of an n-type sensor. Upper panel, the sensor grains (blue circles) placed in a reference atmosphere (here, dry air) interacting with the oxygen ions and/or molecules (green circles), which entrap the electrons (red circles) at the sensor grain surface (the external border of the light blue annulus), subtracting them from the grain bulk (blue circle), enlarging the depletion region (light blue annulus) and consequently increasing the grain–grain potential barrier (BB). Lower panel, sensor exposed to CO (C is light brown circles): the oxygen atoms adsorbed at the grain surface reacts with CO, releasing CO2 in the environment and giving back electrons to the bulk CB, reducing the BB effect.