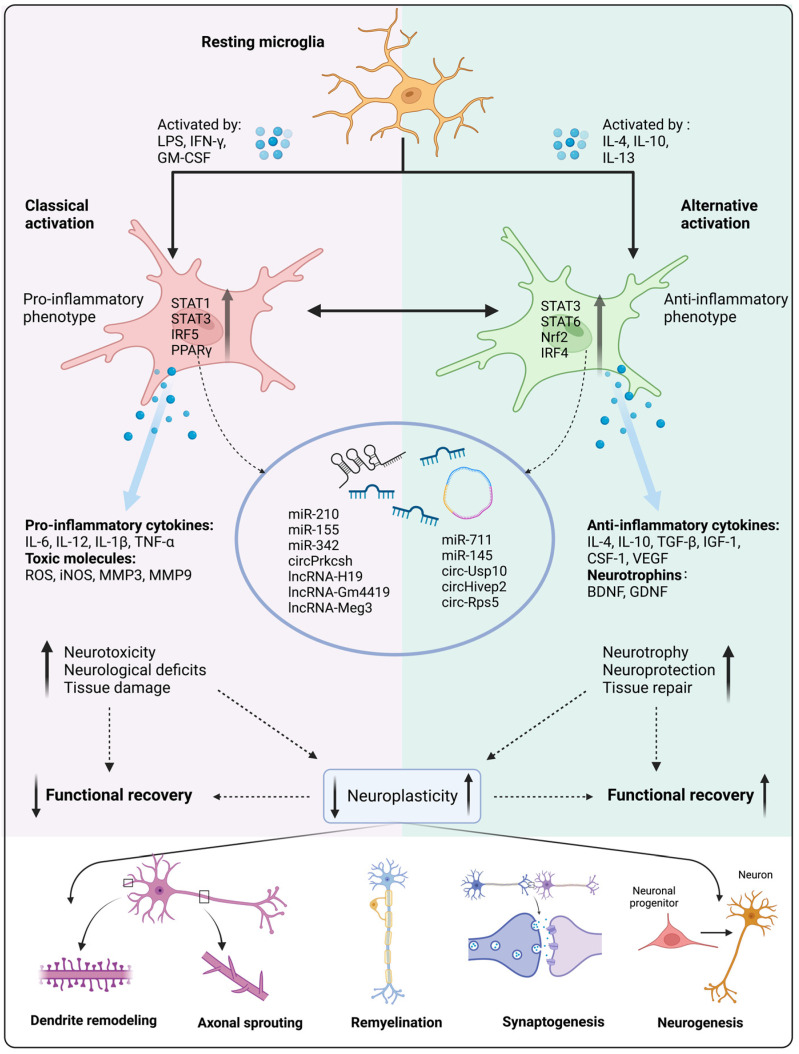
Figure 1.
Microglial activation and polarization affect neuroplasticity and functional recovery. Under pathological conditions, microglia can be activated by specific cytokines that upregulate transcription factors of downstream signaling pathways, thereby resulting in pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory phenotypic polarization. Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) expression also contributes to direct microglial polarization. Pro-inflammatory microglia tend to release pro-inflammatory factors and toxic molecules, which leads to increased neurotoxicity, neurological deficits, and tissue damage, ultimately leading to attenuated neuroplasticity and functional recovery. Conversely, anti-inflammatory microglia release anti-inflammatory factors and neurotrophins, resulting in increased neurotrophy and neuroprotection, thereby enhancing neuroplasticity and functional recovery. LPS, lipopolysaccharide; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL-4, interleukin-4; IL-10, interleukin-10; IL-13, interleukin-13; STAT1, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; IRF5, interferon regulatory factor 5; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; STAT6, signal transducer and activator of transcription 6; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 ; IRF4, interferon regulatory factor 4; IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-12, interleukin-12; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; ROS, reactive oxygen species; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; MMP3, matrix metalloproteinase 3; MMP9, matrix metalloproteinase 9; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; CSF-1, colony-stimulating factor-1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; GDNF, glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; Meg3, maternally expressed gene 3; Usp10, ubiquitin specific peptidase 10. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 1 March 2023.