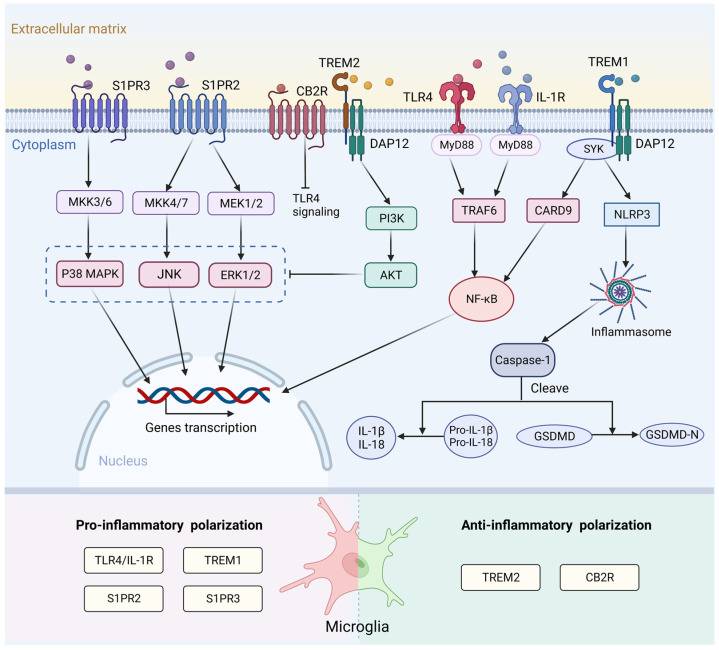
Figure 2.
Surface receptors and the signaling pathways associated with microglia activation following stroke. After binding to endogenous ligand, TLR4 and IL-1R activate the MyD88/ NF-κB pathway to increase the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and induce a pro-inflammatory response. S1PR2 and S1PR3 affect microglial M1 polarization through the ERK1/2 and JNK pathways and p38 MAPK pathway, respectively. TREM1 can activate the downstream CARD9/NF-κB and NLRP3/Caspase-1 signaling pathway to promote the release of inflammatory factors. TREM2- DAP12 interaction activates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, which can inhibit TLR4 signaling by blocking MAPK cascade. CB2R exerts anti-inflammatory effects after stroke. This mechanism may be related to inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; IL-1R, interleukin-1 receptor; MyD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; S1PR2, sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2; S1PR3, sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; p38 MAPK, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; TREM1, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1; CARD9, caspase recruitment domain family member 9; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3; TREM2, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2; DAP12, DNAX activation protein 12; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT, protein kinase B; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MKK3/6, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3/6; MKK4/7, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4/7; MEK1/2, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2; SYK, spleen tyrosine kinase; TRAF6, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL-18, interleukin-18; GSDMD, Gasdermin D. Created with BioRender.com.