Abstract
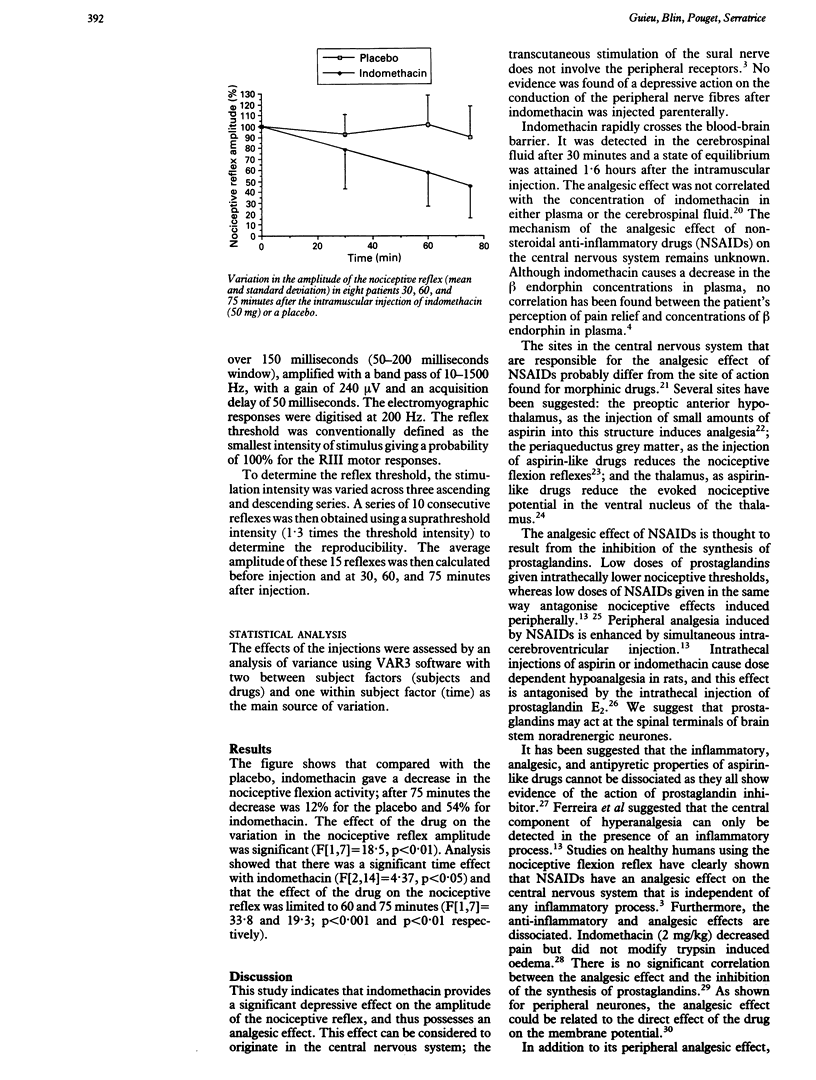
This study investigated whether indomethacin has an analgesic effect on the central nervous system. As analgesics which affect the central nervous system produce a correlated decrease in the subjective sensation of pain and in the nociceptive reflex in humans, the amplitude of the nociceptive flexion of the biceps femoris was studied. Eight patients (six men, two women) aged 35-70 years (mean 51) with rheumatic diseases were included in the study. Each patient was his or her own control and was given a single intramuscular injection of either 50 mg of indomethacin or a placebo. A placebo controlled, double blind experimental design was used. Patients were evaluated before and 30, 60, and 75 minutes after the injection. Seventy five minutes after injection, indomethacin gave a 54% decrease in the amplitude of the nociceptive reflex, whereas the placebo produced a decrease of only 12%. This suggests that indomethacin exerts a depressive effect on the amplitude of the nociceptive reflex and affects the central nervous system as part of its analgesic action.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attal N., Kayser V., Eschalier A., Benoist J. M., Guilbaud G. Behavioural and electrophysiological evidence for an analgesic effect of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, sodium diclofenac. Pain. 1988 Dec;35(3):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(88)90143-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannwarth B., Netter P., Lapicque F., Péré P., Thomas P., Gaucher A. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of indomethacin in humans. Relationship to analgesic activity. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1990;38(4):343–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00315572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandman S., Vandenburg M. J., Jenkins R., Currie W. J. The effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory therapy on plasma neuropeptide concentrations in patients with osteoarthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1985 Feb;24(1):46–52. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/24.1.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burn J. H. Release of noradrenaline from sympathetic endings. Nature. 1971 May 28;231(5300):237–240. doi: 10.1038/231237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson K. H., Helmreich J., Jurna I. Activation of inhibition from the periaqueductal grey matter mediates central analgesic effect of metamizol (dipyrone). Pain. 1986 Dec;27(3):373–390. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(86)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson K. H., Monzel W., Jurna I. Depression by morphine and the non-opioid analgesic agents, metamizol (dipyrone), lysine acetylsalicylate, and paracetamol, of activity in rat thalamus neurones evoked by electrical stimulation of nociceptive afferents. Pain. 1988 Mar;32(3):313–326. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(88)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Prostaglandins and the mechanism of analgesia produced by aspirin-like drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Sep;49(1):86–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomäki H., Martio J., Kaarela K., Kajander A., Koota K., Lehtinen K., Luukkainen R., Martio T., Nissilä M., Nuotio P. Comparison of the analgesic effect of ten nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Br J Rheumatol. 1984 Feb;23(1):61–65. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/23.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keenan D. J., Cave K., Langdon L., Lea R. E. Comparative trial of rectal indomethacin and cryoanalgesia for control of early postthoracotomy pain. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Nov 5;287(6402):1335–1337. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6402.1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIM R. K., GUZMAN F., RODGERS D. W., GOTO K., BRAUN C., DICKERSON G. D., ENGLE R. J. SITE OF ACTION OF NARCOTIC AND NON-NARCOTIC ANALGESICS DETERMINED BY BLOCKING BRADYKININ-EVOKED VISCERAL PAIN. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1964 Nov 1;152:25–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan H., Barker J. L. Salicylate: a structure-activity study of its effects on membrane permeability. Science. 1972 Jun 30;176(4042):1423–1425. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4042.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim R. K. Pain. Annu Rev Physiol. 1970;32:269–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.32.030170.001413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattila M. A., Ahlström-Bengs E., Pekkola P. Intravenous indomethacin or oxycodone in prevention of post-operative pain. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Oct 8;287(6398):1026–1026. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6398.1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maunuksela E. L., Olkkola K. T., Korpela R. Does prophylactic intravenous infusion of indomethacin improve the management of postoperative pain in children? Can J Anaesth. 1988 Mar;35(2):123–127. doi: 10.1007/BF03010650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramwell P. W., Shaw J. E., Jessup R. Spontaneous and evoked release of prostaglandins from frog spinal cord. Am J Physiol. 1966 Oct;211(4):998–1004. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.4.998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schady W., Torebjörk H. E. Central effects of zomepirac on pain evoked by intraneural stimulation in man. J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;24(10):429–435. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1984.tb01815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taiwo Y. O., Levine J. D. Prostaglandins inhibit endogenous pain control mechanisms by blocking transmission at spinal noradrenergic synapses. J Neurosci. 1988 Apr;8(4):1346–1349. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-04-01346.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willer J. C., De Broucker T., Bussel B., Roby-Brami A., Harrewyn J. M. Central analgesic effect of ketoprofen in humans: electrophysiological evidence for a supraspinal mechanism in a double-blind and cross-over study. Pain. 1989 Jul;38(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(89)90065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willer J. C. Studies on pain. Effects of morphine on a spinal nociceptive flexion reflex and related pain sensation in man. Brain Res. 1985 Apr 1;331(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90719-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


