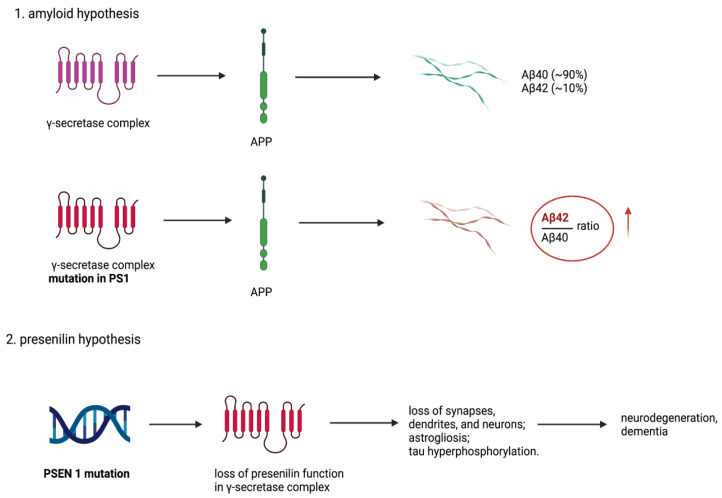
Figure 1.
The comparison between amyloid and presenilin hypotheses. The amyloid hypothesis proposed that mutation in PSEN1 results in presenilin dysfunction, thus change in γ-secretase activity resulting in relative increase of the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio, which is significantly increased in AD pathologies. The presenilin hypothesis does not exclude the amyloid hypothesis but complements it. It presents theory that PSEN1 mutation and following loss of presenilin normal activity in brain triggers neurodegeneration and dementia also without coexisting amyloid formation. Created with BioRender.com.