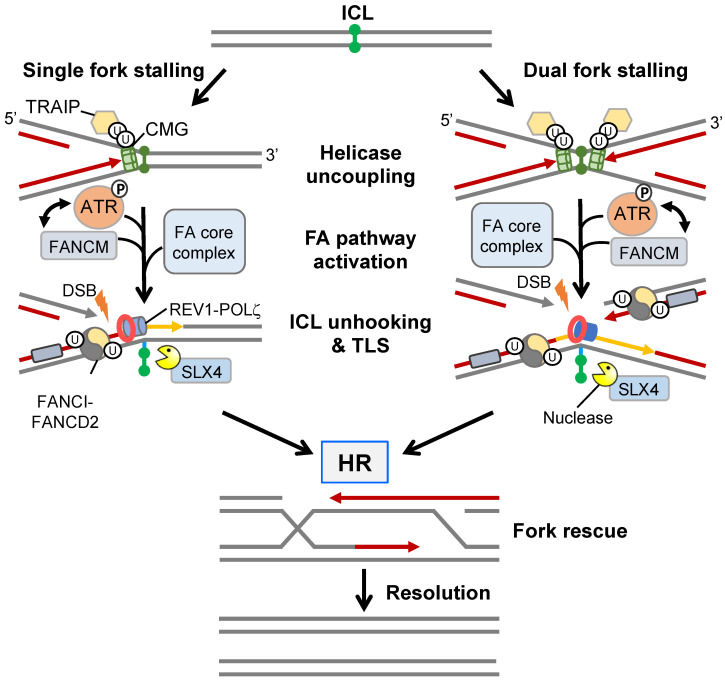
Figure 4.
ICL repair by the FA pathway. The repair of an ICL in S-phase is initiated by a single fork stalling event or convergence of two stalled forks surrounding an ICL locus. After TRAIP-mediated disassembly of the CMG-replisome, the FANCM complex recognises the DNA crosslink and recruits members of the FA core complex and ATR, the latter facilitating a positive feedback loop with FANCM. The FA core complex monoubiquitylates dsDNA-bound FANCI-FANCD2 serving as the hub for the recruitment of structure-specific nucleases that, in cooperation with SLX4, incise the ICL site on both sides (5′ and 3′) of one parental strand generating a DSB in the opposite daughter chromatid. TLS polymerases (e.g., REV1 and POLζ) bypass the unhooked ICL restoring strand integrity of the first chromatid. The remnant ICL is subsequently removed by NER or BER, while the restored parental strand is used as a template for HR-mediated DSB repair.