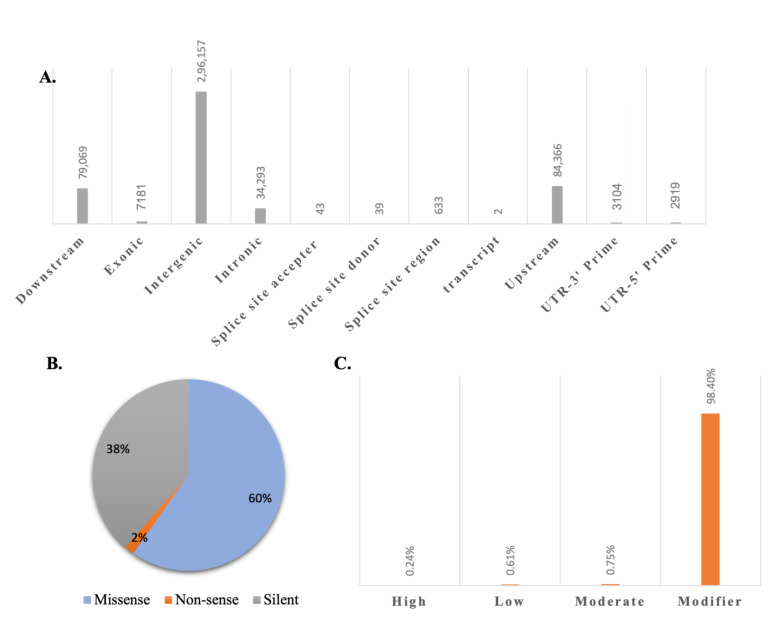
Figure 4.
Number of variants in S. lycopersicum cv. Pusa Ruby genome classified (A) based on genomic region in which they are present, (B) by functional class of effects (in percent), (C) by impact (in percent). Variants can be divided into 11 classes based on position in the genome. These include the following mutations along with their contribution in the Pusa ruby genome: 1. downstream of the gene (15.57%), 2. in the exonic region (1.41%), 3. in the intergenic region (58.32%), 4. in the intronic region (6.75%), 5. in the splice acceptor site (0.008%), 6. in the splice donor site (0.007%), 7. in the splice site (0.12%), 8. mutation hits a transcript (0.0003%), 9. Upstream of a gene (16.6%), 10. variant hits 3′ prime untranslated region (0.61%), and 11. variant hits 5′ prime UTR (0.57%). Based on functional class, the mutations can be missense, non-sense, or silent, the majority being missense (60%) here in the Pusa Ruby genome. (C) Based on impact, the variants can have a high, low, moderate, or no effect. The variants with no effect are defined as modifier here, which also account for the majority (98.4%).